Summary:
Jackson Hole marks the end of the investors’ summer and a beginning of a challenging several weeks.
The abandonment of national business leaders from Trump’s advisory board and strong words by Republican Senator Corker, followed by the dismissal of the controversial Bannon, could be a turning point.
Neither Yellen nor Draghi may not even address the current policy stance as they discuss the topic at hand, “Fostering Dynamic Global Economy”, which lends itself to structural issues.
The US dollar sold off for the first seven months of 2017 and then spent most of the past month consolidating those losses. The Federal Reserve’s Jackson Hole Symposium likely marks the end of the market’s summer, and the consolidation phase. The next several weeks may prove to be more challenging for investors than the past several weeks.
JapanIt is the confluence of events more than economic data that will shape the investment climate. The Jackson Hole confab takes place at the end of the week. At the end of the following week is the EMU’s flash August CPI and the US jobs report, then Norway’s national election, followed by the ECB meeting. The Fed and BOJ hold policy-making meetings two weeks later, which is days before the German election. When the US Congress comes back from its summer holiday, it will have a short window to lift the debt ceiling and approve new spending or risk missing debt servicing payments and government shutdown. Except for Japan’s CPI and the flash eurozone PMI, the economic data in the week ahead are unlikely to attract more than passing attention. Headline CPI in Japan has firmed in recent months, but even if it ticks up to 0.5%, matching a two-year high, it is nothing about which to get excited. The GDP deflator, despite the strong growth (1.0% in Q2 quarter-over-quarter, to lead the G7) remains negative and the targeted core CPI measure (~0.4-0.5%) is well below not only well below the BOJ’s target, but lags behind targeted measures in the US (core PCE deflator 1.4% and the ECB’s headline rate of 1.3%). In the mishmash of policies, the central banks have more or less the same quantitative target for inflation, but the quantities they measure are quite different (dare one say incomparable?). |
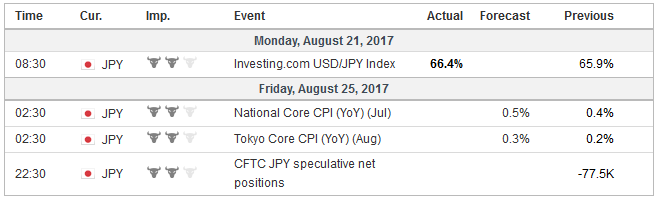
Economic Events: Japan, Week August 21 |
EurozoneThe eurozone economy continues to expand at a sufficient rate to absorb some of the spare capacity, and the output gap is closing. While the regional economy appears to be continuing to operate at strong levels, the momentum has waned. A small gain or a small rise in the composite PMI will be consistent with this assessment and may not be much of a market factor. If it were just the real economy, one wag, noted, the ECB would be ending its extraordinary policies. And if it were just the acting, Mrs. Lincoln would have enjoyed the theater. The vast majority of the ECB still appears to believe that the economy still needs extensive monetary support. Draghi has a fine line to walk, which is even more of a reason why the Jackson Hole forum is a proper venue to talk about the need for structural reform, an important hobby horse of his, but not the nuances of ECB monetary policy. In September, the ECB is likely to announce an extension of its asset purchases into next year at a slower pace (we suspect 30 bln euros a month down from 60 bln presently and 80 bln initially). However, as the record of the July meeting showed, officials are sensitive to the market prematurely tightening financial conditions. |
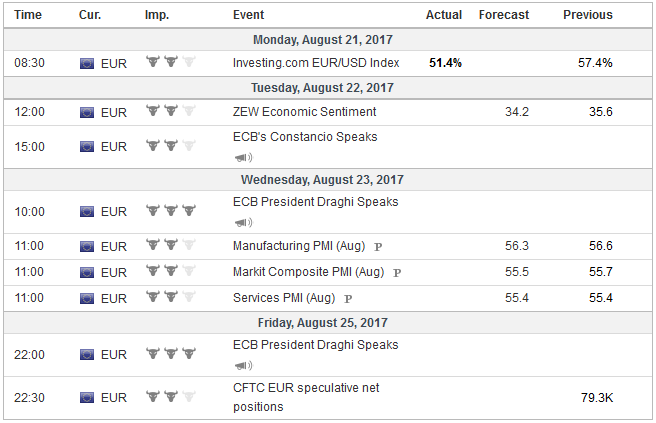
Economic Events: Eurozone, Week August 21 |
United StatesThe Fed’s challenge lies in the other direction. Financial conditions have eased despite its efforts to systematically, but gradually, remove accommodation by lifting the Fed funds target, now four times during this cycle that began in December 2015. The market is pricing in a little more than a one-in-three chance of another hike this year. The market may be under-appreciating the Fed’s resolve, and the weaker dollar and easier financial condition add to the pressure for it to act. There is a battle between the Fed and investors. Officials have warned investors that its concern about asset prices have increased. The Fed has said in word and deed that the current economic conditions warrant a slightly less negative real Fed funds rate. Perhaps, we too easily forget that the Fed has three goals, not just the dual mandate. References to financial conditions have appeared more regularly in individual speeches by Fed officials, it seems. Its minimax strategy of its own trilemma means that the growing risks to financial stability (inappropriate financial conditions for the set of economic conditions) offset some of undershoot of the inflation objective, especially given the continued absorption of labor market slack, broadly understood. The official schedule of the events at Jackson Hole will not be available until August 24, the evening before the event. However, it has already been reported that Yellen will speak on Friday, August 25 (10:00 am ET). To the extent she says anything about the current situation, it does not appear likely that she would deviate much from the thrust of Dudley’s recent comments. The topic at hand lends itself to a larger discussion about growth and productivity. It is an opportunity to trot out her own hobby horse about the important steps that need to be done to increase participation in the workforce. |
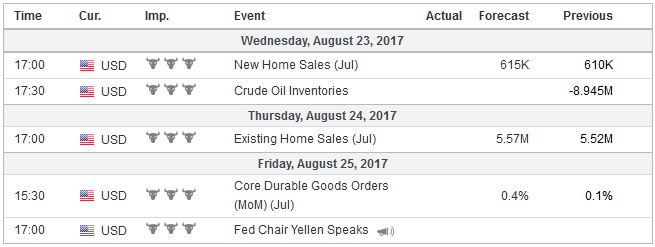
Economic Events: United States, Week August 21 |
Switzerland |
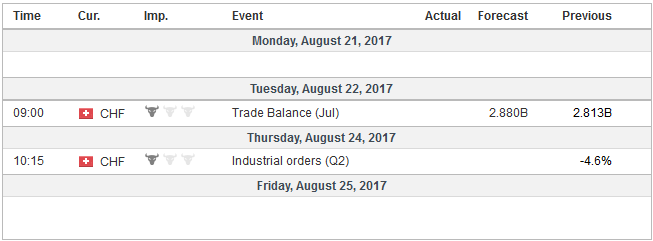
Economic Events: Switzerland, Week August 21 |
There are two other factors that are not to be found on most calendars that could potentially overshadow other drivers in the week ahead. The first is the drama in Washington. Many business leaders who had been on advisory panels quit over a disagreement with how the President handled a domestic terrorist incident. In addition to the two panel that the White House subsequently disbanded, reports indicate that more than half the members of the 15-member Digital Economy Board of Advisers (initially set up by Obama).
Like all modern political movements and parties, Trump’s Administration reflects a coalition. Until now many national business leaders were willing to work with him, even if they were not in full agreement because the economic agenda of deregulation, tax reform, and infrastructure spending was something they could get behind. The prospects have dimmed, given the mess made of healthcare reform and intra-party conflict within the Republican Party, which is trying to exploit its majority rather than make bipartisan deals. One needs not be Machiavelli to see that the perceived reputation risk had increased.
This may be one of the most significant blows to the Trump Administration. And compounding the fracture, was the strong message by Republican Senator Corker, an early Trump supporter. We have tended to downplay the low-level of support in the national polls because drilling down showed his base was intact. Recent events suggest his base is cracking. Controversial adviser Bannon was dismissed before the weekend in what seemed like a sacrificial gesture or an indulgence.
For investors, a key is whether the voice of the business camp of the Trump’s coalition, personified in Cohn, is stronger or weaker. Rumors of his resignation helped trigger, alongside the Fed’s upgraded concern about asset prices, the second largest sell-off in the S&P 500 this year on August 17. Investors may remain sensitive to the shifting balance of influence within Trump’s Administration.
At the same time, it is just another part of the drama and does nothing to find sufficient common ground between the interests represented by the Freedom Caucus and the more moderate Tuesday Group. A weakened president and weak Congress (ineffective majority) do not lend themselves to kind of deal making that is necessary for the normal function of government and the innovations needed to keep the economy competitive.
The second potential destabilizing impulse may come from renewed action in the Korean Peninsula. The bellicose rhetoric has been silenced, but a new round of intimidating actions are about to start. On August 21 the annual Ulchi Freedom Guardian military exercises between the US and South Korean forces that are joined by other nations that reportedly include mock decapitation strikes where the leadership of North Korea, including Kim, are killed and the use of nuclear weapons.
Estimates suggest that at least 80k troops participated in last year’s exercise. Last year, North Korea responded by launching a ballistic missile from a submarine, demonstrating second strike capability. In the 1990s, the some of the exercises were used as bargaining chips that were used to negotiate an agreement aimed to contain North Korea’s nuclear development, which it violated.
It is difficult to see a military solution to the North Korea’s acquisition of nuclear capability including delivery. The broad strategy of deterring the proliferation of nuclear weapons has nevertheless been fairly successful. Most countries do not have the nuclear capability nor are they striving for it. Nevertheless, North Korea acquisition is the most threatening to the US perhaps since China itself acquired such capability.
The ultimate solution may not lie with bilateral talks between the US and North Korea, but between the US and China. North Korea is spurring a response that is undermining China’s nuclear capability. South Korea, Japan, and the US are developing, deploying and upgrading missile defense. It is a bit like a game of football, where sometimes what determines the outcome is offense and sometimes defense. Ostensibly, the deployment of missile defenses by US allies could limit China’s first and second strike capabilities.
The resolution of Pyongyang runs through Beijing. Trump seems to recognize this and may help explain such tentative steps to address trade and currency issues. Last week’s executive order on intellectual property rights gave headline writers plenty of fodder about the coming trade war. It does no such thing. It is a small baby step. It passes the issue to the US Trade Representative who has been asked decide whether to have an investigation. Even if a decision to investigate is made, which is most likely will be, the investigation could take over a year. And even if their investigation is completed, it does not mean action will be taken, as with steel.
New NAFTA negotiations just began, there are ongoing investigations into China’s practices (e.g., aluminum), and countless other ongoing efforts that are apparently being handled by under-staffed offices. At the same time, on August 22, the US and South Korea will begin talks to re-open the five-year-old free-trade agreement. The US complaint is that since the agreement US exports have actually fallen and the bilateral deficit has doubled.
Lastly, equity markets traded heavily in the second half of last week. The marginal investment dollar has not come to the US this year but instead was drawn to the Europe and Emerging Markets. A decline in equities would likely weigh on the euro and emerging market currencies more than the dollar. US T-bills and gold are often the safe havens in equity slides. Gold flirted with the top end of its five-month trading range near $1300 before the weekend and was turned back.
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next postTags: #USD,$EUR,$JPY,Gold,Korea,newslettersent,SPY