Summary:
Spain and Portugal need to make some relatively small budget adjustments or will be denied some transfer payments.
Spain’s political situation is fluid, but another window of opportunity to break the logjam is at hand.
The euro seems immune to these fiscal developments; some retracement objectives are in sight.
 The eurozone finance ministers have accepted the EC’s recommendation that Spain and Portugal not be fined for their fiscal excesses. A few weeks ago, the EU Commissioner for Economic Affairs, Moscovici explained that punitive actions would strengthen anti-EU sentiment. However, that consideration did not prevent the EU from threatening to cut off part of the European Structural and Investment (ESI) funds for next year.
The eurozone finance ministers have accepted the EC’s recommendation that Spain and Portugal not be fined for their fiscal excesses. A few weeks ago, the EU Commissioner for Economic Affairs, Moscovici explained that punitive actions would strengthen anti-EU sentiment. However, that consideration did not prevent the EU from threatening to cut off part of the European Structural and Investment (ESI) funds for next year.
The threat of reducing ESI funds can easily be set aside. Both countries have to move toward compliance with the Stability and Growth Pact and enact the policy recommendations of the EU. Portugal must take corrective action to bring the budget deficit to the 3% of GDP threshold. Last year’s shortfall was 4.4%. That seems optimistic, especially if growth is slower than the 1.3% year-over-year pace the government expects.
Spain has until 2018 to bring its budget deficit to 3% of GDP. The deficit stood at 5.1% in 2015. While Portugal elected a left of center government last year, Spain has been unable to break the political logjam. It has held two elections and still has not been able to cobble a government together. However, a potential breakthrough has occurred. The new centrist party Ciudadanos has set conditions for its support.
Previously, Ciudadanos refused to support Rajoy due to unresolved corruption allegations, but its new demands may prove just as onerous for Rajoy and the PP. The demands include a new parliamentary committee to investigate the slush fund that was allegedly used. There are several judicial investigations. Ciudadanos also wants to remove the protections for senior officials and lawmakers from legal cases. Any politician named in a court corruption probe must step down, and the government should be barred from granting pardons in such cases.
Also, a new electoral law is sought that would establish an eight-year term limit for the prime minister and reduce the advantage of rural voter over urban voters. Since the PP does not have a majority, there may be little it can do about the corruption investigations. Parliament could push ahead with this even if the PP did not agree. Therefore it makes little sense for the PP to object. It is giving up something it does not have. The electoral reform is reportedly a more difficult pill for Rajoy to swallow.
Ciudadanos has 32 seats, while the PP has 137. Together they would be seven seats shy of a majority in the 350-member chamber. If Rajoy and the PP agree to the conditions, then pressure turns to the Socialists, which are the second biggest party. They won 85 seats in June. There is some thought to avoid yet another election, the Socialists could abstain, and in so doing, allow a PP-led minority government.
To “demonstrate full compliance with the Pact”, Spain is required to make a 0.5% fiscal adjustment and Portugal 0.25%. The EC is deferring a final decision on suspending structural funds until at least next month. Effective action is expected to be taken and formally report the details in the middle of October, at the same time as they present the draft 2017 budget plans.
No country has been fined for the lack of fiscal progress. Before the Great Financial Crisis, Germany and France avoided similar penalties. On one hand, the absence of fines undermines the credibility of the Stability and Growth Pact. On the other hand, like other rule-based regimes, exceptions and exemptions are built into the rules themselves, like fouls in many sports. Moscovici argues that the rules give room to cancel fines. The Commissioner also noted that more countries respect the rules now than when there were first introduced.
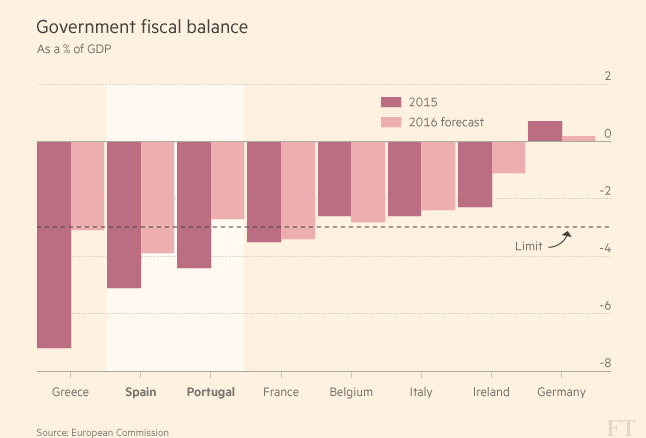
| This Great Graphic comes from the Financial Times. It shows the 2015 deficits for selected European countries and this year’s projections. The projected progress of Greece is remarkable, while Spain is projected to have the largest shortfall. Weak growth prevents the denominator for contributing to the reduction of the deficit-to-GDP ratio. However, that is not the problem for Spain. It grew an enviable 3.2% last year. The median economist forecast is for around 2.8% this year, which, ironically is 0.1% above the government’s estimate. |
ECB bond buying and the quest for yield offset the political and fiscal concerns. In the year-to-date, Spain’s 10-year yield is off 81 bp. A quarter of this was scored in the past month. The yield is off five bp today and is at a new record low of 95 bp. In comparison, Italy’s 10-year benchmark has not penetrated the 1.0% threshold. Portugal’s 10-year benchmark bond has fallen nearly 32 bp over the past month, which has cut the year-to-date rise to 23 bp.
The euro seems immune to these developments. It trended higher from the ECB’s disappointment last December (after reaching ~$1.0525 low) to a high in early-May (~$1.1615). It has trended lower since then and hit a low near $1.09 in response to the UK referendum results. Since then it has managed to close above $1.12 once. A trendline drawn off the May high and the pre-Brexit high (~$1.1430) intersects today near $1.1270. In a week’s time, it is found near $1.1240. The $1.1265 area also corresponds to a 50% retracment of the euro’s decline since early-May (the 61.8% retracement is near $1.1350).
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next post
Tags: EUR/USD,European central bank,Great Graphic,newslettersent,Spain