The prices of the metals hit their lows by the end of April. Gold traded for around $1,685, and is now over $1,900. Silver was around $24, and is now over $28. These are big moves (though of course nothing like bitcoin).
Both metals are subject to the persistent belief that their prices are greatly suppressed. But right now, silver is widely believed to be in a global shortage. We have explained this as a shortage of retail products, most especially one-ounce silver Eagles which currently trade for a premium of 36% or more over the spot price. We have explained the difference between retail products, which depend on finite manufacturing capacity vs. commercial 1000oz bars.
| But today, let’s look at the data. First, here is the silver basis.
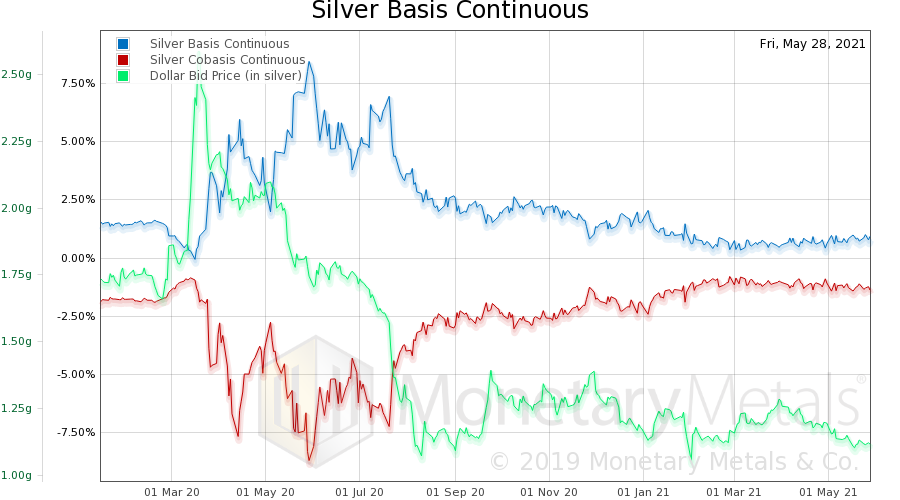
We have zoomed out to show 500 days, and to do this we use the continuous basis (i.e. not a particular contract month, but a mathematically constructed 6-month continuous contract). This lets us see a long period of time, without worrying about where different contracts splice together. And it removes the tendency of each month’s basis to fall as its respective contract approaches expiration (the key to our proof that the banks are not selling futures naked short). The blue line is the basis, the measure of abundance of the metal to the market. The red line is the cobasis, the measure of scarcity. The green line is the price of the dollar, as measured in silver (call us crazy, we believe that a metal which has been money for thousands of years is better suited to measure the irredeemable debt paper of the government, than said debt paper is for measuring money). Notice first the spike up at the onset of the covid crisis, from about 1.8 grams of silver, to a brief high of 2.6g. Then, it goes into a falling trend that has not let up yet. Currently, the dollar is down to 1.12g. When the price of the dollar was spiking (which most people would call a crash in the price of silver), there was no corresponding big move in silver’s scarcity (there was a move, but it’s small). After covid hit, there was a huge change in the apparent scarcity, and the volatility of the apparent scarcity. We have written that this was an anomaly due to covid restrictions and did not indicate massive abundance of silver. |
Silver Basis and Co-basis and the Dollar Price |
|
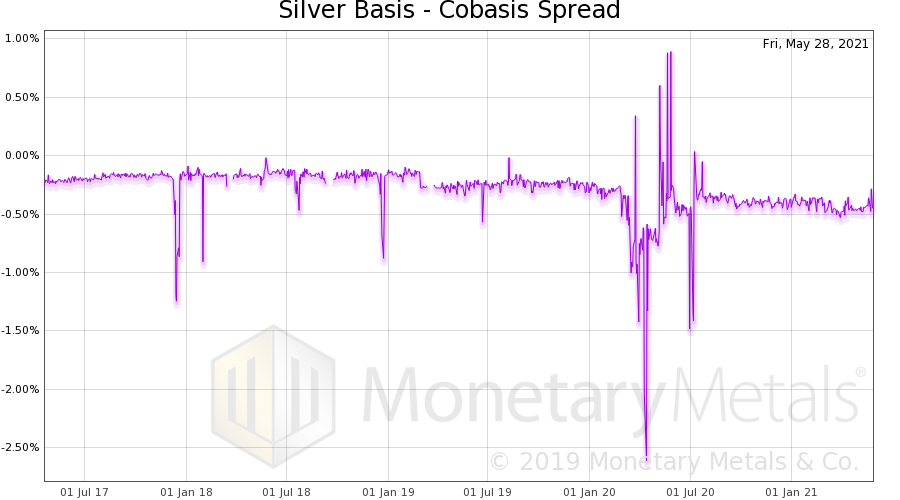
Here is a graph of the spread between the basis and cobasis (basis – cobasis). There is a huge blowout around the beginning of March, 2020. But it not only looks like it is back to normal, but it is tighter than pre-covid. Anyways in 2021, the basis and cobasis have reverted to what looks like a normal spread. And, importantly, these indicators show less abundance and greater scarcity, respectively, than pre-covid. We note the importance, because the price of the dollar is considerably lower (i.e. the price of silver is considerably higher) than it was. A higher scarcity corresponding with a higher price—this is the very picture of a fundamental price move. It is not merely an increase in speculative positions in the futures market, using leverage. It is an increase in the buying of physical metal (if not to the degree promoted in online discussion groups). There is a slow but noticeable drop in scarcity since around the end of February. This should be watched to see if it continues. Silver bulls would not want to see a trend of falling scarcity, especially if the price were to hit a ceiling that it is reluctant to move above. |
Silver Basis and Co-basis Spread |
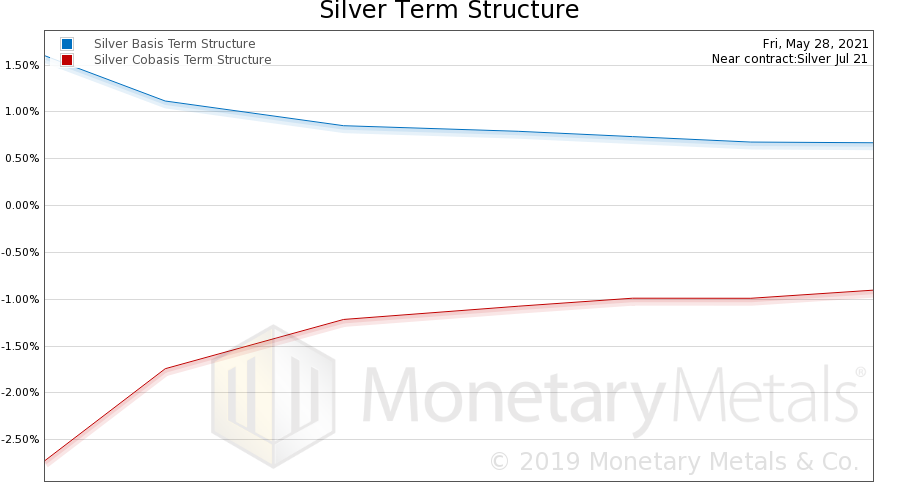
| Here is a graph of the silver term structure. This shows the basis and cobasis for each futures contract, starting with the July contract and going out to September 2022.
Both lines are inverted. That is, there is greater reluctance to buy more distant contracts, compared to nearer contracts. This is akin to an inverted yield curve, where the yield to carry silver for a month is 1.5% annualized but the yield to carry it for 16 months is 0.67%. By comparison, the term structure in gold is basically flat. Just to head it off at the pass, if one believed that the banks were naked selling futures to manipulate the price, that would push down the near-contract basis. That it is high, can only mean only one thing. There is a lot of buying of July silver contracts. And to a less degree, of September. |
Silver Basis and Co-basis, May 28, 2021 |
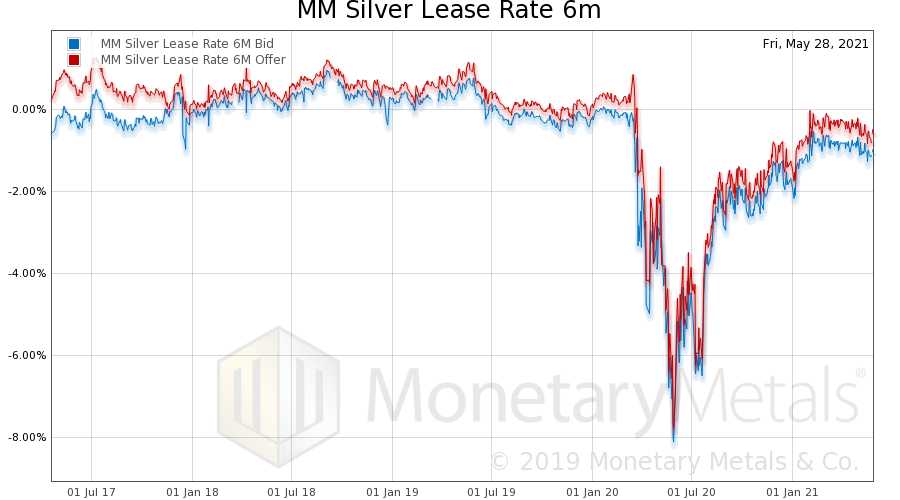
| Let’s look at one last graph. This is a multi-year chart of the silver lease rate. We calculate the lease rate as the point of “zero arbitrage”. It does not include the market maker’s overhead including compliance costs, desired profit, or credit risk premium.
Lower lease rates mean that the metal is more abundant to the market. It was near zero for years, indicating that the basis was high relative to the interest rate. The lease rate is equal to LIBOR – the forward rate. And the forward rate is closely related to the basis. The lease rate apparently plummets to well below zero in the wake of covid. We say “apparently” because no one will lease out silver below zero. Given the incredibly high basis, the “zero arbitrage” point dropped this low. This was an artifact of covid and not a real spike in the abundance of silver, as we said at the time. And note that the silver lease rate is still negative (the gold lease rate is also below zero, though not as far). From this graph, we conclude that one of the following must be true:
We do not believe that silver is so abundant as this would suggest. So scratch this off. |
MM Silver Lease Rate, July 2017 - Jan 2021 |
We are just kidding about 2. Of course, every act by the central planners may have the outcome they desire (or may not), but will certainly have many perverse outcomes that central planners make it their business not to know. If LIBOR were higher, then it would become more expensive for market makers to borrow to buy physical metal and sell futures—to carry silver. With less carrying, which is a response to when speculators bid up futures, the basis would be higher. Thus the silver forward rate would be higher, to go along with a higher LIBOR. And the lease rate might still be underwater.
In Keith’s dissertation, he proved that all acts of government interference in markets reduce the capability of productive people to coordinate their activities in the economy. A negative lease rate, or apparent lease rate, is but one tiny example of this principle.
Once covid lockdowns hit, it became more difficult and slower to ship bars of metal around. This discouraged arbitrages such as carry, as delivery may require shipping the bar. We assume that most of these logistical difficulties are mostly eased now, but this segues into choice D. Basel III dictates a “Net Stable Funding Ratio” which increases a bank’s effective cost of capital to carry gold or silver. This has a similar effect as a higher LIBOR. If we plotted a NFSR-adjusted lease rate, we would expect it to be a positive number.
NSFR-Adjusted forward rate = (LIBOR + increased NSFR costs) – forward rate
Is the increase in cost greater than one percentage point? We would expect so. And if so, then one may safely assume that the lease rate is a point or more higher, to correspond to the higher cost of capital for banks to fund carry of gold and silver.
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next postTags: Basic Reports,Featured,newsletter