Who President Trump ultimately picks as the next Federal Reserve Chairman doesn’t really matter. Unless he goes really far afield to someone totally unexpected, whoever that person will be will be largely more of the same. It won’t be a categorical change, a different philosophical direction that is badly needed.
Still, politically, it does matter to some significant degree. It’s just that the political division isn’t the usual R vs. D, left vs. right. That’s how many are making it out to be, and in doing so exposing what’s really going on.
As usual, the perfect example for these divisions is provided by Paul Krugman. The Nobel Prize Winner ceased being an economist a long time ago, and has become largely a partisan carnival barker. He opines about economic issues, but framed always from that perspective.
To the very idea of a next Fed Chair beyond Yellen, he wrote a few weeks ago, “we’re living in the age of Trump, which means that we should actually expect the worst.” Dr. Krugman wants more of the same, and Candidate Trump campaigned directly against that. As such, there is the non-trivial chance that President Trump lives up to that promise.
Again, it sounds like a left vs. right issue, but it isn’t. The political winds are changing, and the parties themselves are being realigned in different directions (which is not something new; there have been several re-alignments throughout American history even though the two major parties have been entrenched since the 1850’s when Republicans first appeared). Who the next Fed Chair is could tell us something about how far along we are in this evolution.
What Krugman wants, meaning, it is safe to assume, what all those like him want, is simple: success. He believes that the central bank has given us exactly that, therefore it is stupid to upset what works.
This is right here is the very central point of political difference that is pulling the world slowly apart. Krugman offers no evidence for his assertion, that the Fed has performed admirably and successfully, he just states it as if it was so (a common tactic in the mainstream, the fallacy of authority). Whenever challenged on this contention, the argument will always go back to “jobs saved.” |
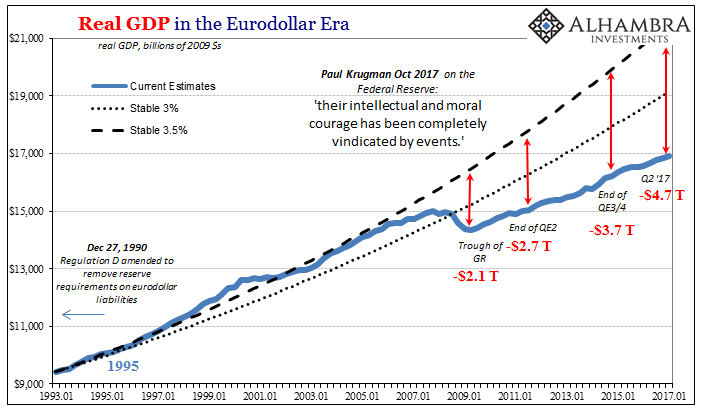
US Real Gross Domestic Product, Jan 1993 - 2017(see more posts on U.S. Gross Domestic Product, ) |
| A worse counterfactual downside is not a rational standard for evaluation in any discipline or context. The only benchmark that should matter is recovery, as any economy facing recession, even an unusually severe one, has to make it back to the prior condition. On that score the Fed has utterly and unambiguously failed.
|
US Commercial Paper, Jan 2001 - 2017(see more posts on Commercial Paper, ) |
| One reason for it is the one thing Economists like Krugman never bring up; the 2008 panic. How can anyone claim the Fed under Yellen or Bernanke performed even minimally well? |
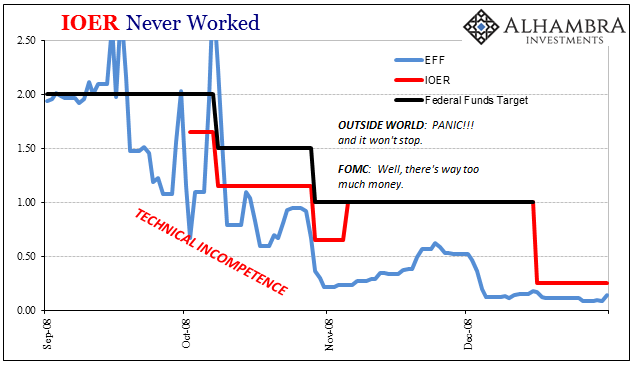
Interest on Excess Reserves Never Worked, Sep - Dec 2008 |
| The very fact that the panic happened at all is a direct indictment on monetary policy and the people who were there during it (you had one job to do!). |
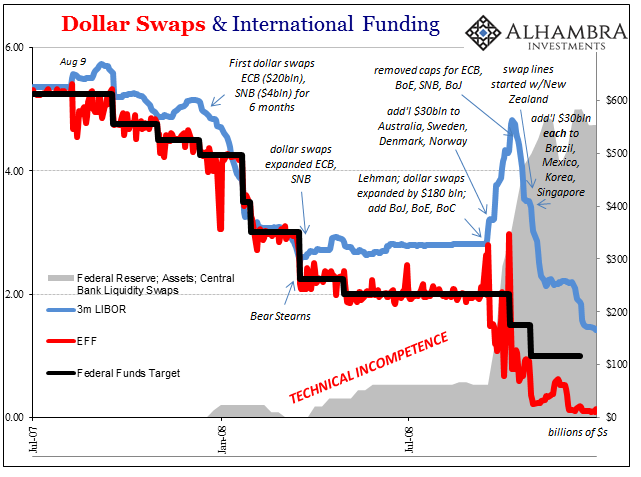
Dollar Swaps and International Funding, Jul 2007 - 2008 |
That’s not really what is at issue here, only it has become one battle in what is a larger war. That struggle is betrayed in Krugman’s own words by which he means to raise up both Bernanke and Yellen as examples of what needs to continue.
This is all really about Economics. It has failed and most publicly so in the form of its principle public adherents in the Federal Reserve piloted by Bernanke and Yellen. The technocratic stars of the faith have been dramatically dimmed by events. Economists are not scientists, clearly, and so they are desperately seeking to circle the wagons by rewriting history; the last ten years weren’t all that bad, and they really could have been worse if it wasn’t for Economics. The irrational, emotional defense for the ideology is what is driving political upheaval, including Donald Trump’s occupying the White House. To most people, Krugman’s ideas and assertions are nonsense. They don’t have to know anything about QE’s effect on the TBA market and dollar rolls, how exactly McDonald’s was borrowing from FRBNY, or what it was that AIG did that ultimately made the Federal Reserve profits. People know the Fed did a bunch of stuff that didn’t work because they can tell there is something very wrong with the economy. |
US Retail Sales, Jan 1992 - 2017(see more posts on U.S. Retail Sales, ) |
And after ten years of being told not to worry about it, or that it was being expertly handled, the people are Fed up with the defense of ideology first at the expense of actual answers. That’s really where we are; Economics has no more solutions (more QE!), therefore Economists have been forced to re-evaluate everything but only along those lines. If Economics can’t solve the problem, then they believe this has to be as good as it gets. And everyone should just stop complaining and appreciate the heroic and inspired effort that “saved” so many “jobs.”
Trump’s candidacy, as Bernie Sanders’, as an ideal was a grave threat to the status quo because it started with the premise that, no, this isn’t as good as it can be and that we need to look for real solutions. Whether he forwards that ideal as President is and has been another matter, and who he picks as Fed Chair might be some small indication of where he currently stands consistent with that idea, or perhaps having second thoughts about it.
The technocracy doesn’t work because it isn’t technically competent (thus 2008).
That’s the real political debate in 2017 and going forward; technical incompetence where the defense of the technocracy refuses to even allow the suggestion that this might be true. I go back to Weimar Germany not because I expect a global hyperinflationary breakdown, but in how that one particular form of systemic breakdown exposed timeless flaws inherent in all economic and financial systems. They all run to some extent on trust and (good) faith:
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next postIn other words, German monetary officials, particularly Reichsbank head Rudolf von Havenstein and Minister of Finance Karl Helfferich, denied that Germany had an inflation problem at all – right up until the end. Minister Helfferich declared that Germany had better gold coverage after the war than before it, despite that more than quadrupling of currency volume. One economics professor, Julius Wolf, wrote in 1922 that, “in proportion to the need, less money circulates in Germany now than before the war.” As much as the easy-to-see Versailles excuse played a part, there can be no doubt that beyond 1921 the German people themselves began to recognize that authorities had no idea what they were doing; worse, they came to see that even though policymakers were inept and incompetent, officials themselves would never admit as much and thus nothing would prevent Germany from its fate. That awakening meant an increase in danger that French occupation could never have unleashed on its own.
Tags: Ben Bernanke,Commercial Paper,currencies,Donald Trump,economy,Federal Reserve,Federal Reserve/Monetary Policy,Janet Yellen,Markets,newslettersent,Paul Krugman,Politics,U.S. Gross Domestic Product,U.S. Retail Sales