The increasing volatility of SNB EarningsAnnual results are not really definite. Given that the SNB accumulates foreign currencies with interventions, they have huge swings. But the SNB may lose 50 billion in one year and win 60 billion in the next year or vice verse. Good years of the Credit CycleThis trend was stopped in 2016, even without the need for a cap on the franc. But one should consider that we are in the good years of the credit cycle now. Bad quarters like the one in Q4/2018 are rare now. Franc will rise again with crisis or inflationWith a new financial crisis or a with a big rise of inflation, the run into the Swiss franc will start again. And this at an exchange rate that is not digestible for the SNB.
And this will lead to a massive SNB loss around 150 billion CHF. However, we are not there yet: Inflation is low and interest rates even lower. |
[ProfitLoss2019] |
Some extracts from the official statement.
|
Income statement, 1 January–30 September 2019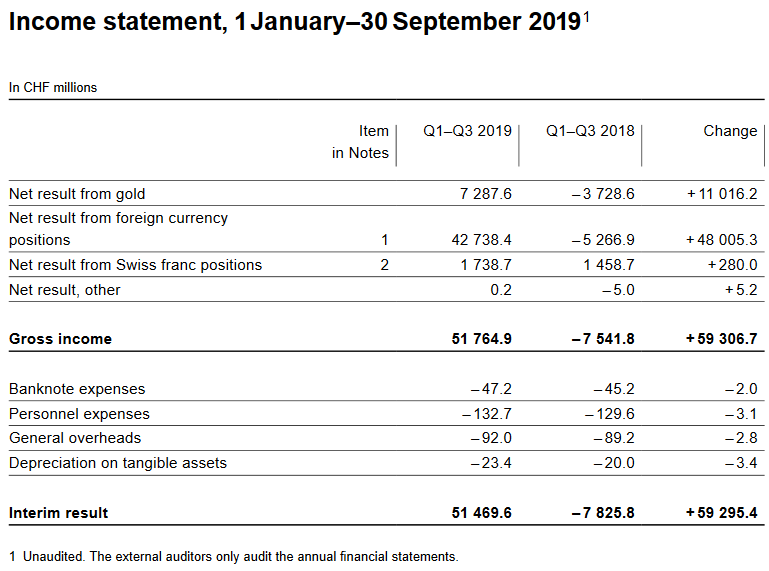 Source: snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Profit on foreign currency positionIn a period of low interest rates, asset prices rise, last but not least because of margin debt. When the Fed raised rates in 2018, the SNB had a loss of 15 billion francs. Fortunately for the SNB, the Fed stopped raising rates in 2019, on the contrary U.S. rates went down. Rising asset prices implies that the SNB obtains a profit.
The following numbers are in billion Swiss Francs.
|
SNB Profit on Foreign Currencies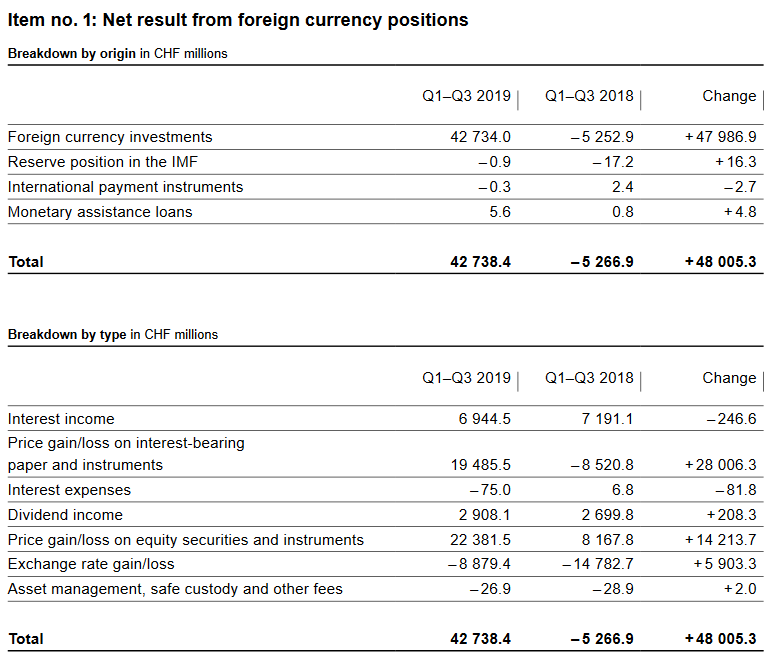 Source: snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Valuation loss on gold holdings
Percentage of gold to balance sheetThe percentage of gold has risen to 5.76% thanks to higher prices.
Balance Sheet The balance sheet has expanded by over 46.1 bn. francs by 5.67%. Especially during summer there were bigger SNB interventions.
|
SNB Balance Sheet for Gold Holdings for Q3 2019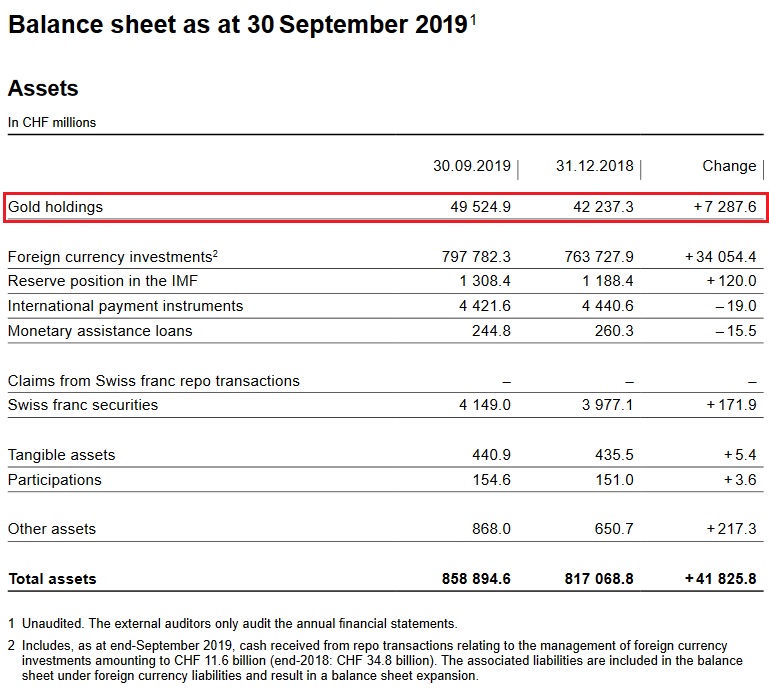 Source: snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Profit on Swiss franc positionsThe SNB maintains its profitability, last but not least, thanks to the reduction of the profitability of banks. When too many funds arrive on their accounts, they must deposit them on their sight deposit account at the SNB.
Negative Interest ratesFurthermore, the SNB harms the Swiss economy, when it reduces the profits of Swiss banks by negative interest rates. But with this measure she maintains her own profitability. The SNB obtained slightly less money for negative rates, while sight deposits were slightly up (see below). The reason might that banks better use their exoneration from negative rates. Still, as compared to the FX profits or gains on equities, this number is relatively low.
|
SNB Result for Swiss Franc Positions for Q3 2019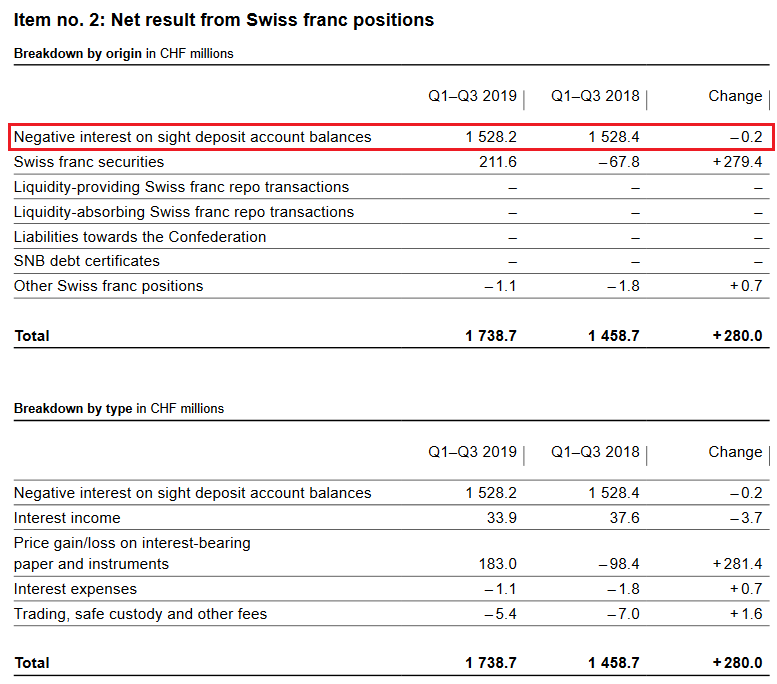 Source: snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SNB LiabilitiesElectronic Money Printing: Sight Deposits Sight deposits is the biggest part of SNB interventions. In the third quarter, the SNB intervened again, increasing sight deposits and its debt towards the Swiss state.
Paper PrintingBanknotes in circulation: -2.54 bn francs to 79.7 bn. CHF This old form of a printing press, today a less important form of central bank interventions. It showed that safe-haven Swiss francs, e.g. 1000 franc bank notes are currently less in demand than previously. Provisions for currency reservesThe SNB seems to think that the price gains in bonds and in stocks are forever sure. Only about 10% of the paper gain is put into the provisions for potential bigger FX losses. |
SNB Liabilities and Sight Deposits for Q3 2019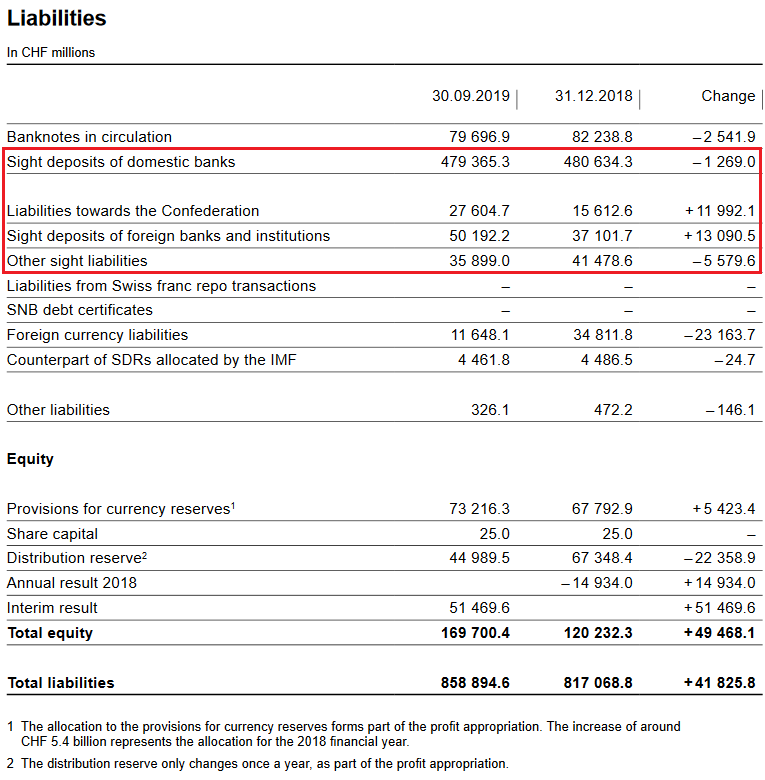 Source: snb.ch - Click to enlarge |
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next post
Tags: newsletter,SNB balance sheet,SNB equity holdings,SNB Gold Holdings,SNB profit,SNB results,SNB sight deposits,Swiss National Bank


































1 comments
Stefan
2019-11-01 at 12:02 (UTC 2) Link to this comment
It is worth reminding the public at all times that the so-called distribution reserve should be counted towards the provisions for currency reserves in light of the enormous growth of said currency reserves from 10% of GDP in 2006 to almost 120% of GDP today.
The downward risk on the foreign currency reserves of 800 bn CHF are in essence:
Appreciation of the CHF by 5% in one year: : -40 bn CHF
Appreciation of the CHF by 10% in one year: : -80 bn CHF
Rise in interest rates of +2%: -70 bn CHF
For comparison: the entire equity of the the SNB including the distribution reserve amounts to 170 bn CHF or 20% of the balance sheet total.
It is comforting to know that the SNB’s equity is in no immediate danger of being wiped out. This being said, the sheer size of the risk is apt to tame any desire to redirect SNB funds to other use, a desire that all too easily infiltrates the political discussion when media reports abound regarding the profits and distribution reserve of the SNB.