We do not like Purchasing Power or Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) as measurement for currencies. For us, the trade balance decides if a currency is overvalued. Only the trade balance can express productivity gains, while the REER assumes constant productivity in comparison to trade partners.
Who has read Michael Pettis, knows that a rising trade surplus may also be caused by a higher savings rate while the trade partners decided to spend more. This is partially true.
Recently Europeans started to increase their savings rate, while Americans reduced it. This has led to a rising trade and current surplus for the Europeans.
But also to a massive Swiss trade surplus with the United States, that lifted Switzerland on the U.S. currency manipulation watch list.
To control the trade balance against this “savings effect”, economists may look at imports. When imports are rising at the same pace as GDP or consumption, then there is no such “savings effect”.
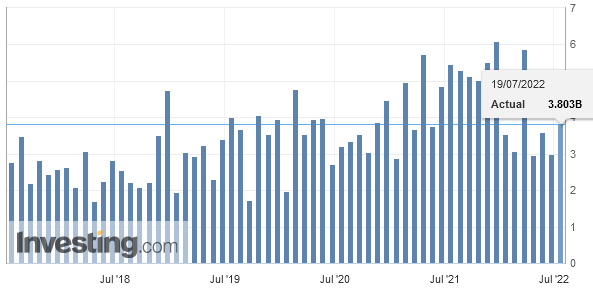
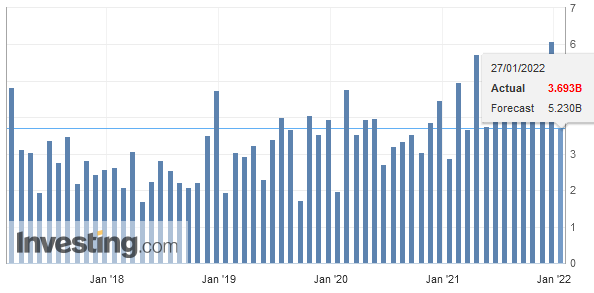
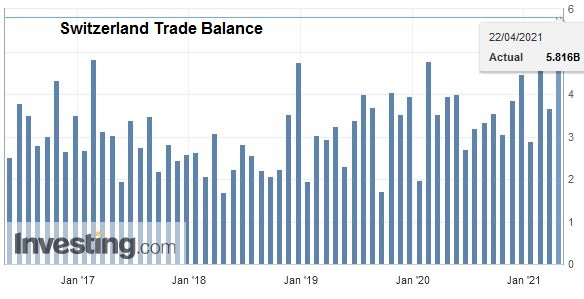
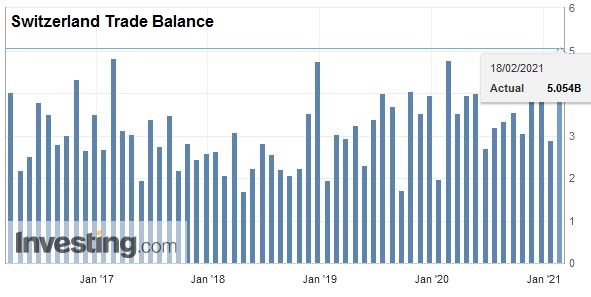
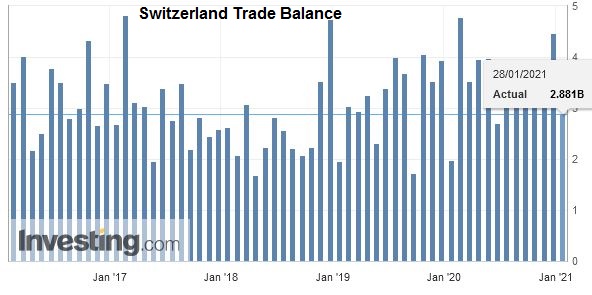
After the record trade surpluses, the Swiss economy may have turned around: consumption and imports are finally rising more than in 2015 and early 2016. In March the trade surplus got bigger again, still shy of the records in 2016.
Swiss National Bank wants to keep non-profitable sectors alive
Swiss exports are moving more and more toward higher value sectors: away from watches, jewelry and manufacturing towards chemicals and pharmaceuticals. With currency interventions, the SNB is trying to keep sectors alive, that would not survive without interventions.
At the same time, importers keep the currency gains of imported goods and return little to the consumer. This tendency is accentuated by the SNB, that makes the franc weaker.
Texts and Charts from the Swiss customs data release (translated from French).
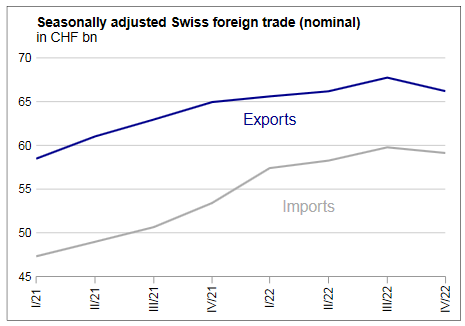
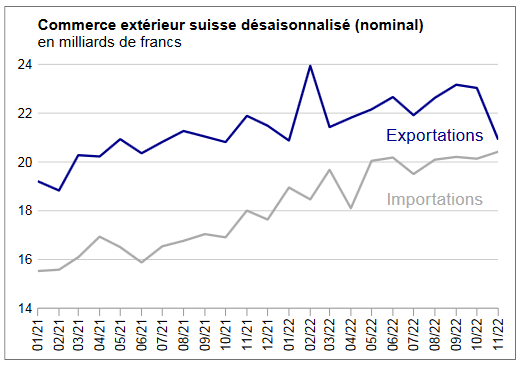
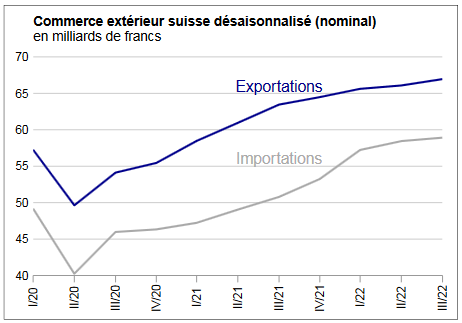
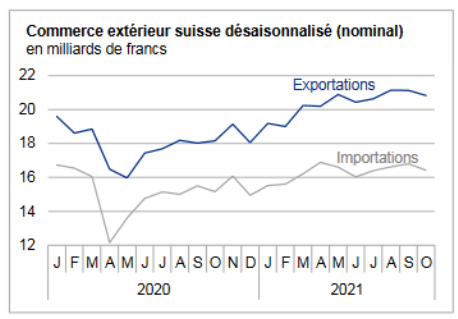
Exports and Imports YoY DevelopmentIn February 2018, exports increased by 1.8%, confirming their positive trend. After their January record, imports fell back (-9.8%). However, they continued to grow at a high level, at 16.1 billion francs. At the entrance, the flagship markets Europe and North America led the result. ▲ The positive trend continues for the four pillars of export ▼ US imports: lowest result in four years ▼ Pharma and aircraft explain declining imports |
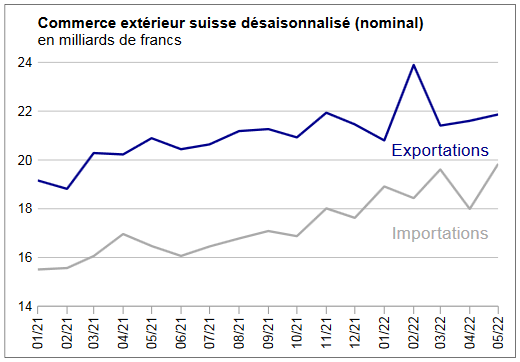
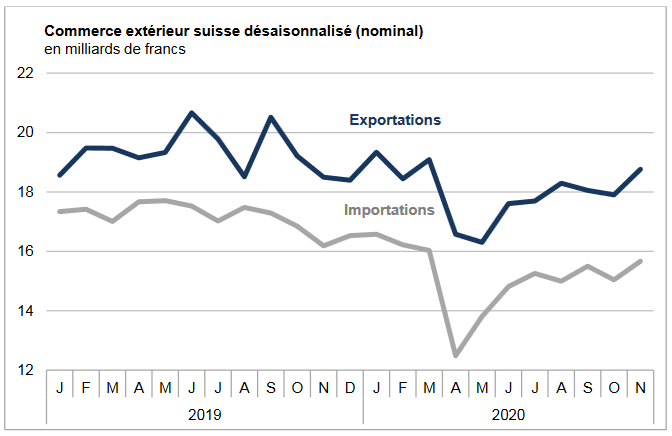
Swiss exports and imports, seasonally adjusted (in bn CHF), February 2018(see more posts on Switzerland Exports, Switzerland Imports, )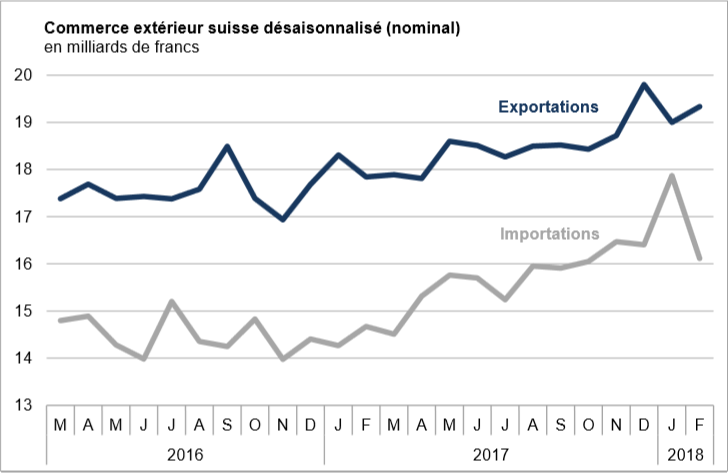 Source: Swiss Customs - Click to enlarge |
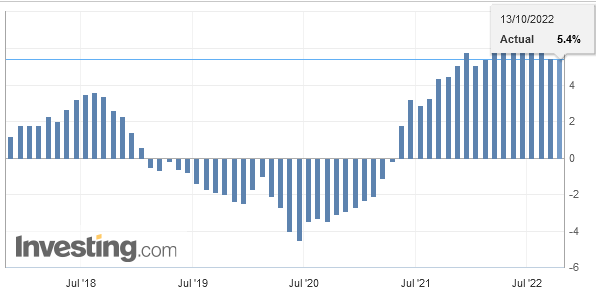
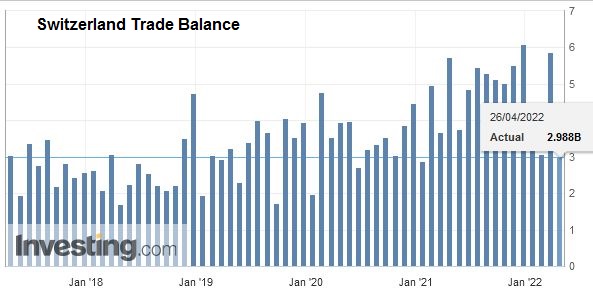
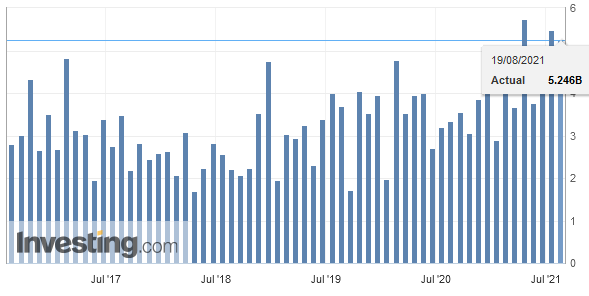
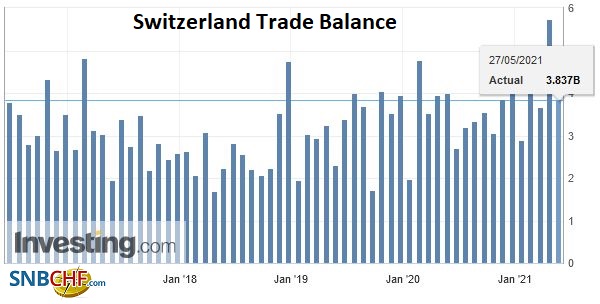
Overall evolutionIn February 2018, seasonally adjusted exports increased by 1.8% (real: + 2.3%), confirming their upward trend. On the other hand, imports contracted by 9.8% (actual: -9.5%) compared to the record result of January. However, they continued to grow at a very high level (CHF 16.1 billion). The trade balance closes with a surplus of 3215 million francs.
|
Switzerland Trade Balance, Feb 2018(see more posts on Switzerland Trade Balance, ) Source: Investing.com - Click to enlarge |
ExportsExports: 95% of “made in Europe” growthConfirming their positive trend in previous months (+ 4.1%, +343 million francs), chemicals and pharmaceuticals were the main contributors to export growth. With a jump of 21% (+241 million francs), the active ingredients played the role of locomotive in chemistry-pharma. The “Other” group also contributed to growth, with an increase of 22.6% for jewelery (+186 million francs). Conversely, sales of machinery and electronics, precision instruments and metals fell for the second month in a row. Nevertheless, MEM products continued to evolve at a high level. Watchmaking has bent its back for the first time in four months. Nevertheless, the third exporting sector still shows a trend towards the top. From a geographical point of view, the rise in exports was 95% based on Europe (+ 3.1%). Sales with the third largest market, North America, also increased (+ 1.7%, Canada: +60 million francs). Despite a 2% decline, sales to Asia still show an upward trend. European growth was largely boosted by Spain (+ 39.1%), Italy and France. Conversely, the United Kingdom plunged 23.6% to 704 million francs, the lowest level since September 2014. Asian side, despite their setbacks, China (-13%) and Japan ( -6.4%) continued to ride a positive wave. |
Swiss Exports per Sector February 2018 vs. 2017(see more posts on Switzerland Export, Switzerland Exports by Sector, )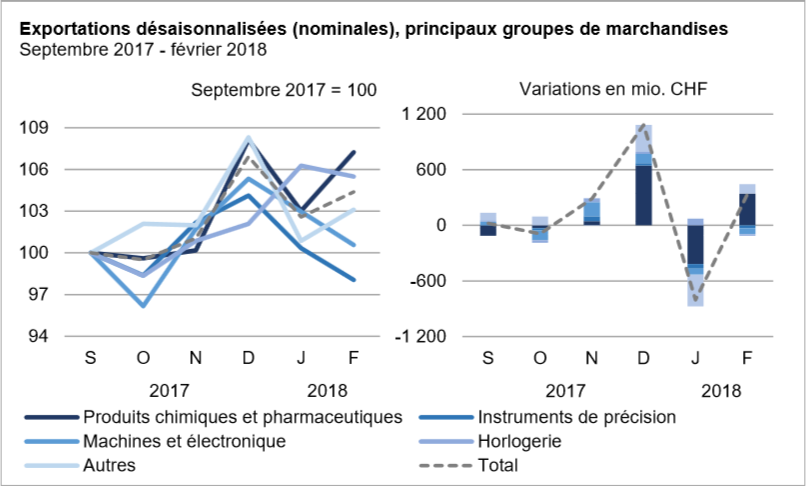 Source: Swiss Customs - Click to enlarge |
ImportsImports: the previous month’s record blacks the tableIn February 2018, the chemicals-pharmaceuticals and vehicles sectors accounted for 93% of the decline in imports. As a result of a base effect (record figures in January), imports of chemicals and pharmaceuticals fell by 979 million francs. Medicines and active ingredients fell by respectively 452 and 419 million francs. Vehicle imports (previous month: imports of airliners) dropped by 656 million francs to 1.3 billion, the lowest level in two years. The machinery and electronics sector and the metals sector have stalled compared to the peaks of the previous months. The decline in imports took hold on the North American (-43.3%, USA: -45.3%) and European continents. Conversely, receipts from Asia increased by 11.3%, boosted by the doubling of shipments from the Middle East (jewelery). Imports from North America fell back to May 2014 levels (878 million francs), penalized by aeronautics and chemistry-pharma. The reverse of the Old Continent came, among others, from the United Kingdom (-196 million francs), Italy (-129 million) and Ireland (-115 million). |
Swiss Imports per Sector February 2018 vs. 2017(see more posts on Switzerland Imports, Switzerland Imports by Sector, )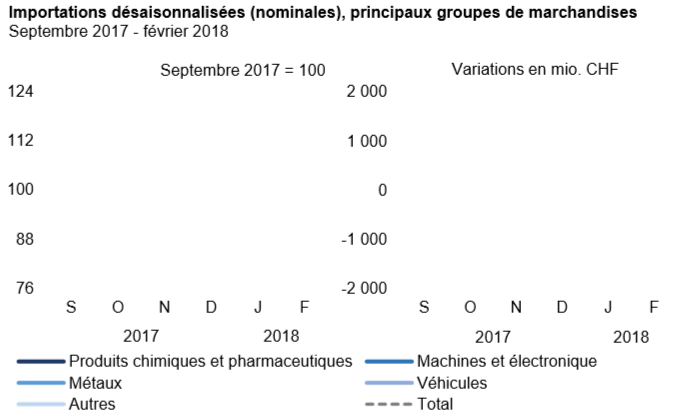 Source: Swiss Customs - Click to enlarge |
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next post
Tags: newslettersent,Switzerland Export,Switzerland Exports,Switzerland Exports by Sector,Switzerland Imports,Switzerland Imports by Sector,Switzerland Trade Balance