Swiss FrancThe Euro has risen by 0.41% to 1.1566 CHF. |
EUR/CHF and USD/CHF, February 06(see more posts on EUR/CHF, USD/CHF, )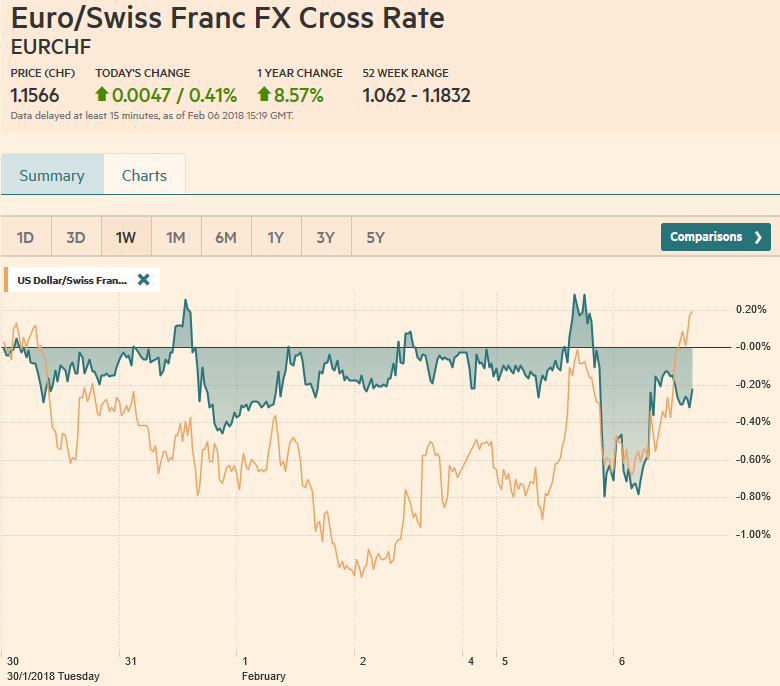 Source: markets.ft.com - Click to enlarge |
FX RatesAfter the dramatic fall in US equities, Asian equities followed suit. The MSCI Asia Pacific Index fell 3.4% following Monday’s slide of 1.7%. European bourses gapped lower and spent most of the morning moving higher, though large gaps remain. At its worst, the Dow Jones Stoxx 600 was off about 3.3%, and at the time of this writing, it is half as much. US equities initially extended yesterday’s losses, but the S&P 500 has turned higher in the European morning in very volatile activity. The US 10-year note yield fell nearly 14 bp yesterday. Asian and European bond yields have fallen today. Australia’s 10-year yield is off 11 bp to 2.82%, while core bond yields in Europe are off four-five basis points and the peripheral yields are off two-three basis points. US Treasuries yields have stabilized about two basis points above yesterday’s close near 2.70%. Just like portfolio insurance has been cited in many narratives for aggravating the 1987 equity market crash, so are volatility-linked strategies and products being a factor in the current meltdown. These products allowed investors to be short volatility in expectations of continued calm. It has been a virtual cash register. Two such exchange traded products failed yesterday. |
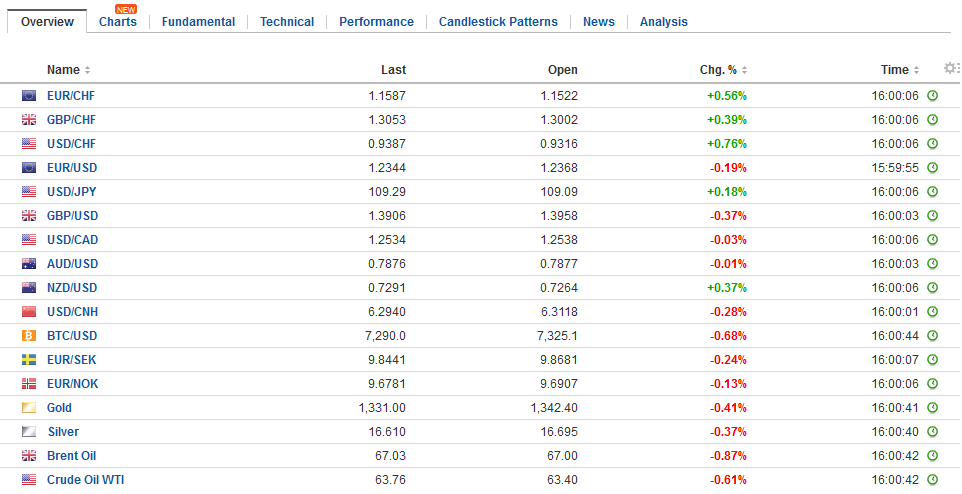
FX Daily Rates, February 06 |
| Yet it is important the price action in perspective. As dramatic as it is, the major bourses have given up last month’s gain and a little be more. The record point drop in the Dow Jones Industrials leaves if off 1.5% for the year. The S&P 500 is off less than 1% coming into today. Italy’s FTSE Milan is the only G7 equity market still up on the year (~2.9%). If one was concerned that equity valuations were elevated, the recent drop may have simply skimmed off some froth.
The news stream is relatively light today and the implications of the equity drop is being mulled by investors. The initial reaction seems to be two-fold. One if the broad de-risking, and the second is the economic implications. The idea is that the sharp decline in equities will impact consumer sentiment and undermine the wealth impact. Given the strength of the US, EMU and Japanese economic momentum, it may take more than giving back a few weeks’ worth of gains to pose a serious challenge. Moreover, there is no urgency for central banks. The Fed does not meet for a little more than a month, and the ECB’s course is set via 30 bln a month in asset purchases through September. The BOJ’s Kuroda argued against any near-term rate increase, arguing inflation is simply too low. |
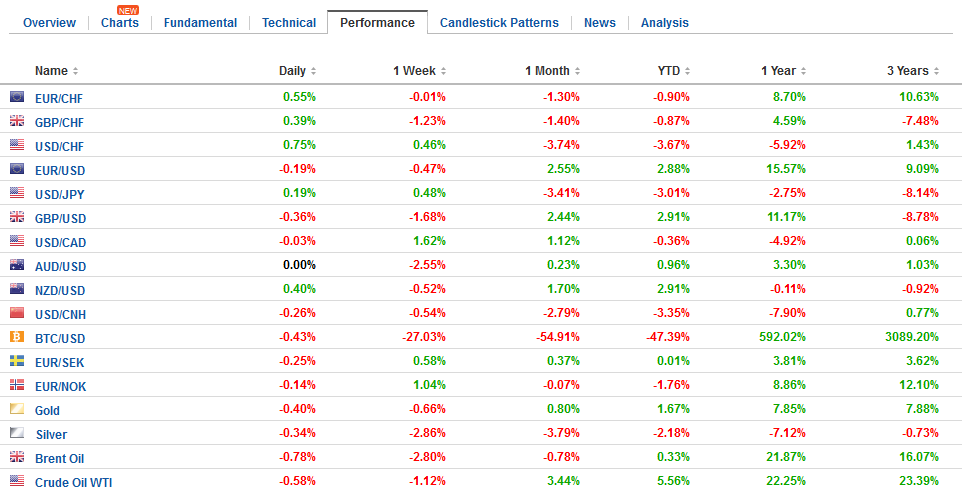
FX Performance, February 06 |
GermanyGerman factory orders jumped 3.8% in December, a gain of more than five-times the median forecast in the Bloomberg survey. The November series was revised to show a 0.1% decline instead of a 0.4% fall. Big ticket items drove the increase, and capital equipment orders from EMU members jumped 18.5%. Domestic orders rose a still-healthy 0.7%. |
Germany Factory Orders, Dec 2017(see more posts on Germany Factory Orders, )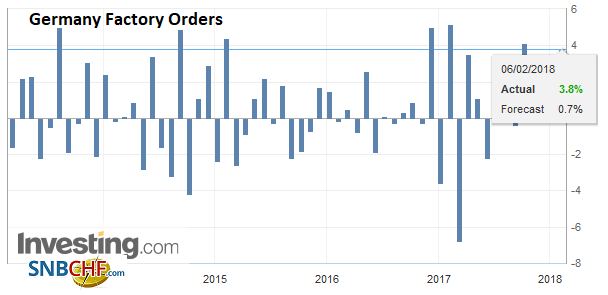 Source: Investing.com - Click to enlarge |
Eurozone |
Eurozone Retail Purchasing Managers Index (PMI), Jan 2018(see more posts on Eurozone Retail PMI, ) Source: Investing.com - Click to enlarge |
United States |
U.S. Trade Balance, Dec 2017(see more posts on U.S. Trade Balance, )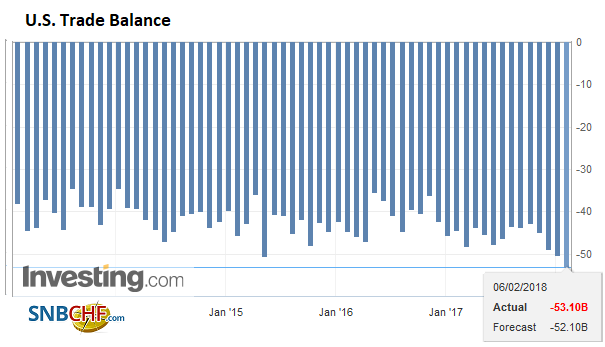 Source: Investing.com - Click to enlarge |
To the extent that investors can shift their attention from the equity drama, Germany is center stage today. First, after a series of work stoppages, IG Metall struck a deal with employers. It is a complicated deal with one off payments and covering 27 months. The headline of a 4.3% wage deal over 27 months, seems to downplay the wage increase, which is something like 3.7% for 2018 and a little more (~4.0% in 2019). The deal also includes greater flexibility in terms of hours– a right to reduce the workweek to 28 hours for two years, with the option to return to full-time later. One issue is whether the deal can be used as a boilerplate for other industries that facing negotiations this year, including chemical, construction, rail, and telecom workers.
Talks between the Merkel’s CDU/CSU and the SPD are in overtime, but officials seem optimistic that a deal can still be struck that would avoid a minority government and new elections. The latest polls warn that the SPD may have slipped below 20% public support. The SPD members get a final say on whatever agreement may be struck, but the threat of new elections seems to be a poison chalice.
Separately, we not that today is the last day to submit candidates for the vice president of the ECB. Ireland has submitted its central banker Lane as a candidate. Spain’s de Guindos was thought to be the front-runner, and apparently did not compete for Eurogroup head to position for the ECB post. Many ECB officials seemed uneasy about a finance minister and one without a deep economic background to be in such a senior position at the ECB. De Guindos has not been formally nominated, and the Socialists have indicated they will not support his candidacy. This leaves Spain, with a minority government, in a difficult position.
The Reserve Bank of Australia met earlier today. It was the first of three major central banks to meet this week (RBNZ and BOE meetings still to come). There were no surprises. The cash rate was left unchanged at 1.5%. The statement seemed upbeat on growth and encouraging on labor market developments, but was caution on housing and consumption.
In North America, the equity markets are the key focus, while both Canada and the US report December trade figures. We know from the initial release of Q4 17 US GDP, that net exports were a significant drag. The December trade balance is expected to have widened to $52.1 bln from $50.5 in November. While a widening of the trade deficit is likely to irk some US Administration officials, we argue that the narrowing of the energy balance means that the non-oil balance is deteriorating faster than appreciated. The average shortfall in 2017 through November was $46.7 bln. Canada’s trade’s trade deficit is expected to be little changed from November C$2.5 bln deficit. The average deficit in the first 11 months was C$1.9 bln.
Separately, Canada reported the IVEY PMI for January, and it will be compared to December’s 60.4 reading. The Fed’s Bullard speaks on the US economy and monetary policy today, while another seven Fed officials speak before the end of the week.
Graphs and additional information on Swiss Franc by the snbchf team.
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next postTags: equities,EUR/CHF,Eurozone Retail PMI,Germany,Germany Factory Orders,newslettersent,SPY,U.S. Trade Balance,USD/CHF