A very insightful post from Bloomberg. We added some more explanations. We explained that the dollar is currently more overvalued than the Swiss Franc.
Swiss National Bank President Thomas Jordan keeps saying the franc is “significantly overvalued.” And that’s despite the central bank’s record-low deposit rate and occasional currency market interventions.
While the franc is typically a top choice for foreign investors looking for a safe place to park their money, anxieties about the euro area’s debt burden or Brexit aren’t the only factor. The residents of Switzerland — which has a sizable current-account surplus despite its strong currency — are partly to blame because they aren’t moving money abroad, which could help them achieve higher returns.
|
 Swiss National Bank President Thomas Jordan keeps saying the franc is “significantly overvalued.” And that’s despite the central bank’s record-low deposit rate and occasional currency market interventions. - Click to enlarge |
Reason 1: Private Sector Buys Securities in CHF
“Roughly speaking, about half the capital inflows are due to domestic investors, which means they’re contributing in a big way to the strength of the franc,” said Maxime Botteron, an economist at Credit Suisse in Zurich. The following four charts illustrate the state of play.
Households have an ever-greater share of franc-denominated assets.
Switzerland has outperformed the European Union in economic growth from 2008 to 2014. No wonder that the Swiss prefer Swiss securities.
We explained that Swiss will buy foreign securities only when
- foreign rates are significantly higher than Swiss rates (for bonds)
- foreign GDP growth and foreign company profits are significantly higher (for stocks)
|
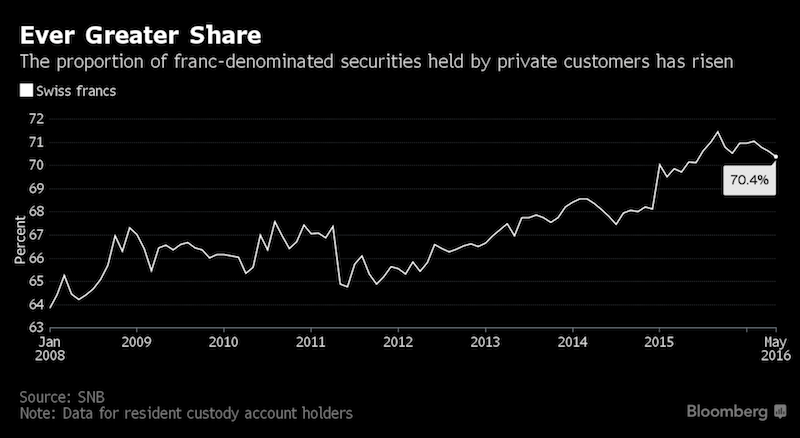 Swiss National Bank President Thomas Jordan keeps saying the franc is “significantly overvalued.” And that’s despite the central bank’s record-low deposit rate and occasional currency market interventions. - Click to enlarge It’s worth noting that the development of that ratio over time doesn’t factor in valuation effects due to changes in the exchange rate. |
Reason 2: Massive Swiss Current Account Surplus
Switzerland’s current-account surplus was nearly 11 percent of gross domestic domestic product at the end of March. That’s a ratio bigger than that of euro-area export powerhouse Germany and compares with a 5.7 percent deficit in the U.K. The euro-zone average is a 3.2 percent surplus.
We explained here that one main reason is the rising Swiss savings rate, while Americans or Europeans save less.
Savings is done in cash or in Swiss securities (reason 1) or -even better – in Swiss real estate, where prices rose by 7% per year until 2014.
|
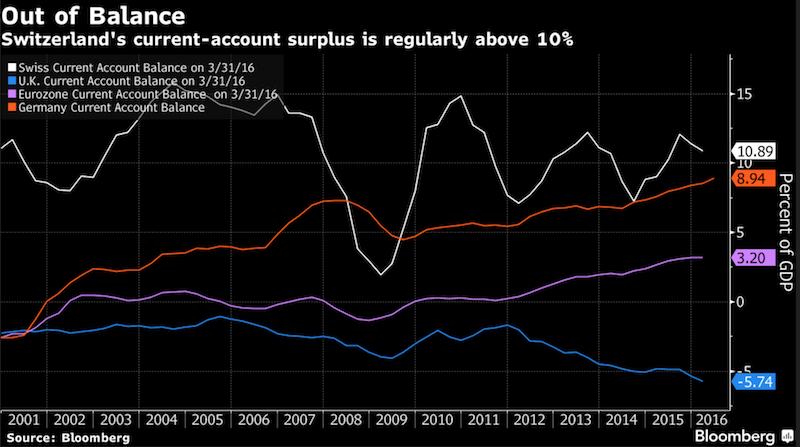 Click to enlarge. |
Reason3: Rate-Differential not big enough
In a bid to drive down yields on franc-denominated assets, the SNB cut its deposit rate to a record low of minus 0.75 percent. Swiss policy makers have threatened to go even more negative if needed. Economists say investors won’t begin to hoard cash to circumvent the charge as long as the rate doesn’t fall below minus 1.25 percent.
We explained that Swiss investors expect a sufficient risk-reward combination, when buying foreign securities. We judge that a rate differential of 1.5% is needed.
Moreover, the majority of Swiss savers are not punished yet with negative rates. |
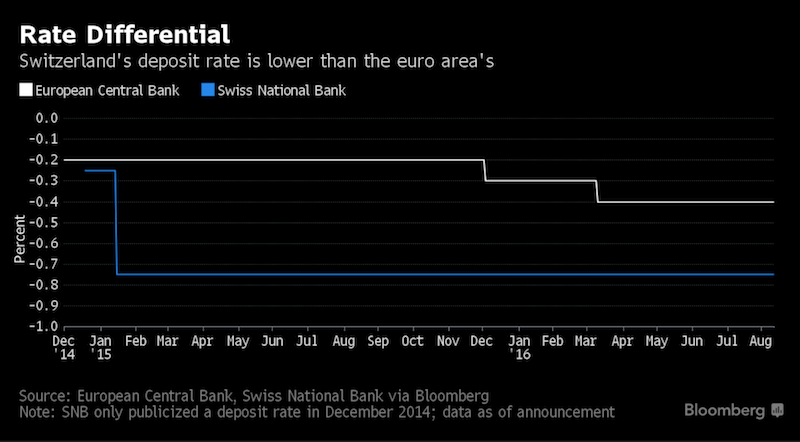 Swiss National Bank President Thomas Jordan keeps saying the franc is “significantly overvalued.” And that’s despite the central bank’s record-low deposit rate and occasional currency market interventions. - Click to enlarge |
Reason 4: Pension Funds Hold (too) many Swiss Franc Investments
Even with negative rates, Swiss pension funds hold the lion’s share of their assets in francs, according to a study by Credit Suisse. As in other jurisdictions, their investment decisions are affected by regulatory requirements.
If the Swiss themselves “were to invest more heavily in foreign assets, that could lessen pressure on the franc and the SNB wouldn’t have to intervene as heavily,” Botteron said. “But that probably would necessitate a change of policy in the euro area, with a widening of the interest-rate differential, which would make euro-denominated assets more attractive again.”
With economists anticipating further ECB stimulus rather than a cutback in stimulus, that doesn’t look to be happening any time soon.
|
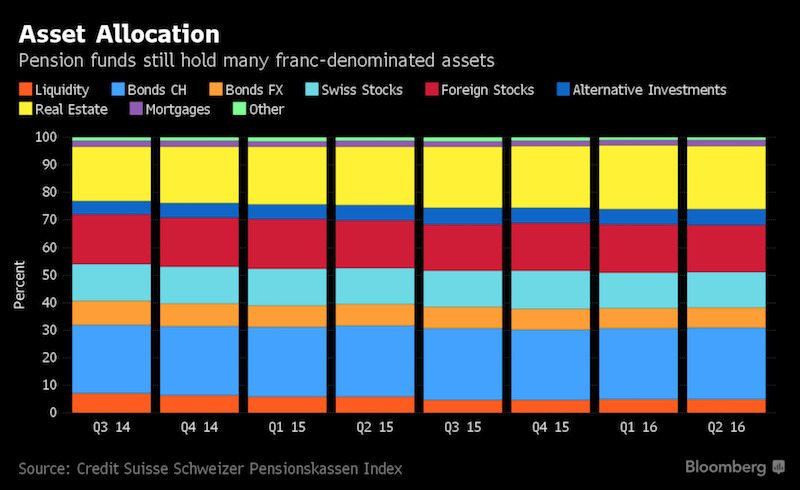 Swiss National Bank President Thomas Jordan keeps saying the franc is “significantly overvalued.” And that’s despite the central bank’s record-low deposit rate and occasional currency market interventions. - Click to enlarge |
The post was originally published by Catherine Bosley (Bloomberg)
Full story here
Are you the author?
George Dorgan (penname) predicted the end of the EUR/CHF peg at the CFA Society and at many occasions on SeekingAlpha.com and on this blog. Several Swiss and international financial advisors support the site. These firms aim to deliver independent advice from the often misleading mainstream of banks and asset managers.
George is FinTech entrepreneur, financial author and alternative economist. He speak seven languages fluently.
Previous post
See more for 1.) CHF FX
Next post
Tags:
Credit Suisse,
Editor's Choice,
newslettersent,
Thomas Jordan