Category Archive: 6b.) Mises.org
The Folly of “Ask What You Can Do for Your Country”
Recently, I was reminded of John F. Kennedy’s most famous line, “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country,” when I heard it among several famous sound bites leading into a radio show segment. It also reminded me that we will hear it more soon, as we are approaching JFK’s May 29 birthday. However, it is worth reconsidering what it means.
Read More »
Read More »
Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic Events
Abstract: Much of Shiller’s new book is about how economic narratives form, spread, and fade. Drawing on medical evidence about the spread of infectious disease, Shiller argues that “economic fluctuations are substantially driven by contagion of oversimplified and easily transmitted variants of economic narratives.” But Shiller ignores the powerful role of monetary disorder, whether in forming the narrative or determining the contagion rate, or as...
Read More »
Read More »
The Japanese Love of Keynesian Economics Might Finally Be Coming to an End
Even those fortunate enough to have escaped infection by the Wuhan coronavirus will by now have noticed one of the virus’ many secondary effects: the disruption of the supply chain. Sick workers at meat plants, closed restaurants, hoarding, and the sudden spike in demand for things like ventilators, masks, and comestibles with long shelf lives have thrown the global flow of goods and services into disarray.
Read More »
Read More »
Why an Economy Can’t Work without Market Prices
It has been a full century since Mises dropped the economic calculation bomb, but the argument apparently still haunts socialists. It should, since Mises managed to show that a socialist economy is not an economy at all but calculational chaos. Yet it is curious that it does, since most have (incorrectly) concluded that Mises’s argument, after decades of debate, was debunked.
Read More »
Read More »
Banking and Monetary Policy from the Perspective of Austrian Economics
The editors are to be heartily congratulated for putting together this book, which covers an impressive range of topics in monetary economics from an explicitly Austrian perspective. Most of the twelve essays are of a very high quality and one will learn much about money and related topics by a careful reading of them.
Read More »
Read More »
Let’s Hope Deflation Is Headed Our Way
The yearly growth rate of the US consumer price index (CPI) fell to 0.4 percent in April from 2 percent in April last year while the annual growth of the producer price index (PPI) plunged to –1.2 percent last month against 2.4 percent in April 2019.
Read More »
Read More »
How Modern Economics Has Lost Its Way: It’s All About the “Unseen”
Economics has lost its way and the study has become both impotent and lacking in relevance. It's easy to see how and why once we recognize that proper economic thinking takes place two steps beyond the apparent. Noneconomists typically take none of these steps, while modern economics has lost the ability to go beyond the first.
Read More »
Read More »
Krugman: We Need More Unemployment—to Save Us from Unemployment
It has been a long time since I read anything by Paul Krugman, and seeing his most recent column simply reminds me why I’ve not missed anything. As both an extreme Keynesian and political partisan, he long ago abandoned economic analysis for something economists should recognize as nothing less than what Mises called metaphysics.
Read More »
Read More »
Economics in Two Lessons: Why Markets Work So Well, and Why They Can Fail So Badly
Economics in Two Lessons: Why Markets Work So Well, and Why They Can Fail So BadlyJohn QuigginPrinceton: Princeton University Press, 2019xii + 390 pp. Abstract: John Quiggin’s Economics in Two Lessons alleges a failing in Henry Hazlitt’s Economics in One Lesson: the absence of a discussion of market failure.
Read More »
Read More »
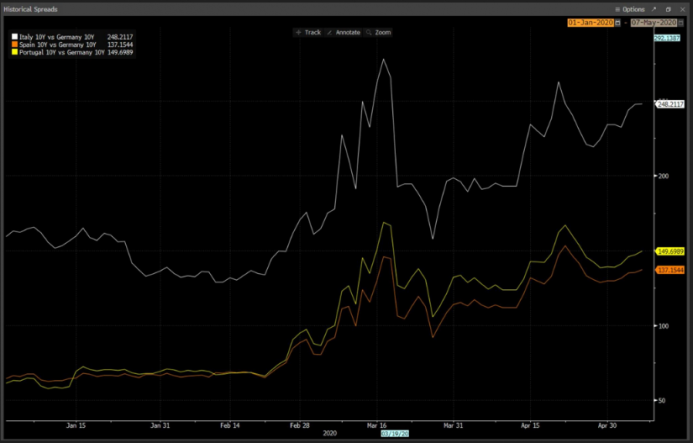
The ECB Has Been Hiding Risk. They Won’t Be Able to Do It Much Longer.
Despite the unprecedented increase in the European Central Bank’s asset purchase program, the spread of southern European sovereign bonds versus German ones is rising.
Read More »
Read More »
Money Supply Growth in April Ballooned to a New High
Fueled by unprecedented quantitative easing, central bank asset purchases, and various stimulus packages, the money supply growth rate ballooned in April to an all-time high. The growth rate has never been higher, with the 1970s as the only period that comes close. It was expected that money supply growth would surge in recent months. This usually happens in the wake of the early months of a recession or financial crisis.
Read More »
Read More »
How Words Like “Essential” and “Need” Are Abused by Politicians
Over the years, one of the most common trump cards used to justify government treating people differently, rather than equally, has been the word need. And when used to override individuals’ ownership of themselves and what they produce, its usage has created confusion rather than clarity. In public discussion, “need” has increasingly morphed into one of its synonyms—essential, as in “essential jobs.” But it still suffers from many of the same...
Read More »
Read More »
How Central Banks and Lockdowns Are Making the Crisis Worse
What typifies the phenomenon of the boom-bust cycle is that it is recurrent. What is the reason for this? Loose monetary policies set the platform for various activities that would not emerge without the easy monetary stance. What loose monetary policy does here is to engineer the transfer of real savings from wealth generating activities to artificially stimulated activities, which we can label as bubble activities.
Read More »
Read More »
Crisis or Opportunity? To Politicians, It’s the Same Thing
Forget performing William Shakespeare’s Macbeth. The real art form is politicking. They sport taxpayer-funded windbreakers, speak with authority and urgency, and lead a brigade of specialists. When a crisis unfolds, whether it is a hurricane or a virus outbreak, politicians stand before the cameras, appearing to be in control of the situation—but they see an opportunity.
Read More »
Read More »
How Bad Is It?
How bad is it? That is the question on everyone's mind as we come to grips with the economic carnage caused by global economic shutdowns, supply chain disruptions, and ongoing quarantines of million of people. Do we face another Great Depression, or simply a deep recession more like 2008? And equally important, are soft Americans prepared for either? Have we started to process all of this psychologically?
Read More »
Read More »
Ludwig von Mises & “Circulation Credit” Theory of the Trade Cycle
[This article is part of the Understanding Money Mechanics series, by Robert P. Murphy. The series will be published as a book in late 2020.] Starting with Carl Menger’s undisputed role in the “marginal revolution,” which ushered in subjective value theory, the Austrian school has made important contributions that have been absorbed into standard economic theory.
Read More »
Read More »
More Protectionism and Regulation Won’t Fix the Economy
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic and its attendant economic strains, some protectionists and anti-immigration ideologues are trying to take advantage of this opportunity to advance their nationalist agenda. They argue that if the United States had restricted international trade and immigration more thoroughly in the past, as President Trump had fought to achieve, the public health crisis could have been curtailed.
Read More »
Read More »
Three Reasons Why the Eurozone Recovery Will Be Poor
The eurozone economy is expected to collapse in 2020. In countries such as Spain and Italy, the decline, more than 9 percent, will likely be much larger than in emerging market economies. However, the key is to understand how and when the eurozone economies will recover.
Read More »
Read More »
How the Corona Crisis Differs from the 2008–2009 Financial Crisis
There are several important differences between the global financial crisis of 2007–08 (GFC) and the coronavirus crisis (CC). Origin and Nature of the Crisis. The GFC resulted from financial imbalances, primarily the housing bubble, while the CC was triggered by the external negative shock (the pandemic and the following economic shutdown) that dramatically reduced the labor supply.
Read More »
Read More »
When Governments Switched Their Story from “Flatten the Curve” to “Lockdown until Vaccine”
In the early days of the COVID-19 panic—back in mid-March—articles began to appear pushing the idea of "flattening the curve" (the Washington Post ran an article called "Flatten the Curve" on March 14). This idea was premised on spreading out the total number of COVID-19 infections over time, so as to not overburden the healthcare infrastructure.
Read More »
Read More »