Category Archive: 6b.) Mises.org
More than Half of All US COVID-19 Deaths Occur in Only Four States
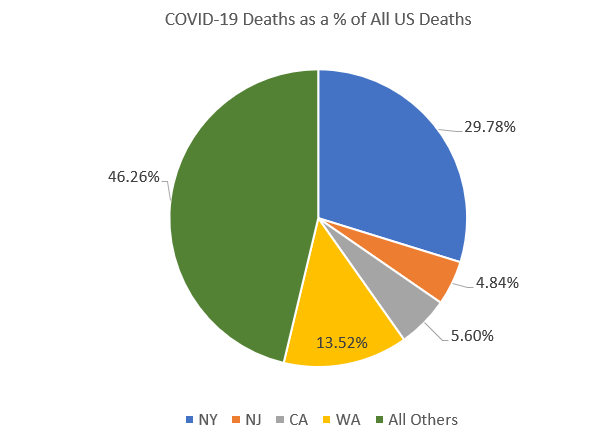
As of March 24, nearly 30 percent of all the COVID-19 deaths in the United States have occurred in New York state. Of the 910 deaths reported so far in the US, 271 happened in New York. Washington State was in second place, with 13 percent of the nation's COVID-19 deaths.
Read More »
Read More »
Diversification versus Risk
It is widely held that financial asset prices fully reflect all available and relevant information, and that adjustments to new information is virtually instantaneous. This way of thinking which is known as the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) is closely linked with the modern portfolio theory (MPT), which postulates that market participants are at least as good at price forecasting as any model that a financial market scholar can come up with,...
Read More »
Read More »
Central Bankers Are Running Out of Options
Corona fears have shifted the world’s central banks into hyperdrive. Talk more, do more, lend more—and buy everything that moves. One after the other, the major central banks took to the barricades, manned the canons, fired their bazookas, and every other military metaphor you can think of.
Read More »
Read More »
The European Central Bank Is Being Stretched to Its Breaking Point in Italy
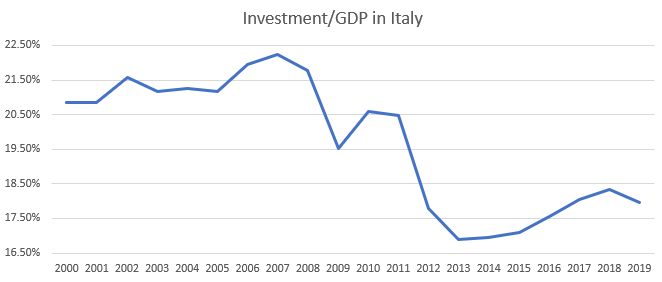
When Mario Draghi’s tenure was approaching its end, I argued for a sterner governor for the European Central Bank (ECB); hence, I was not even slightly enthusiastic when Draghi’s successor turned out to be Christine Lagarde—a patent dove, as can be inferred from her ideological proximity to a famous Keynesian like Olivier Blanchard.
Read More »
Read More »
Diseases Are Bad. Government-Forced Shutdowns Are Often Worse.
However high the death rate of the COVID-19 coronavirus becomes, the governmental response to the threat will be even more dangerous. If the current blockade of economic life continues, more people will die from the countermeasures than from the virus itself. In a short time, the basic supply of everyday goods will be at risk. By interrupting the global transport and supply chains, important medicines will be missing and food supplies will be...
Read More »
Read More »
In Spain You Can’t Use Your Own Back Yard. Police Make Sure of It.
The last days and weeks of the coronavirus epidemic give an interesting insight into the human psyche. Elementary liberties are restricted all over the world, such as the freedom of movement or private property. Yet most people accept these restrictions without blinking, as the state declares their indispensability.
Read More »
Read More »
No, Technology Shocks Aren’t Behind Recurring Business Cycles
Economic fluctuations, also known as business cycles, are seen as being driven by mysterious forces that are difficult to identify. Finn Kydland and Edward C. Prescott (KP), the 2004 Nobel laureates in economics, decided to attempt to find out what these forces were.1 They hypothesized that technology shocks are a major factor behind economic fluctuations and demonstrated that a technology-induced shock can explain 70 percent of the fluctuations in...
Read More »
Read More »
Government Is No Match for the Coronavirus
The coronavirus is reminding everyone that you cannot rely on government and that ultimately it is the private sector that will provide the solutions. Many nonmedical government officials and members of the media are predicting massive cases of COVID-19 and death, when in fact no one can predict the outcome.
Read More »
Read More »
Financialization: Why the Financial Sector Now Rules the Global Economy
To read or watch the news in today's world is to be confronted with a wide array of stories about financial organization and financial institutions. News about central banks, interest rates, and debt appear to be everywhere.
Read More »
Read More »
Money Supply Growth Climbs to 37-Month High
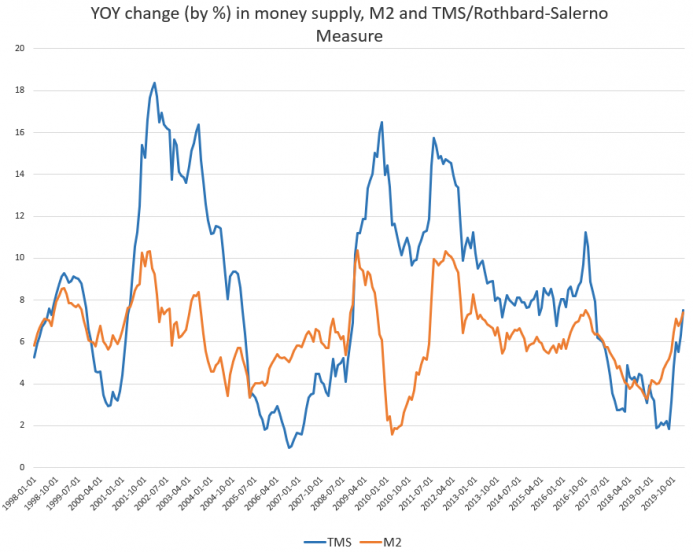
The money supply growth rate rose again in February, climbing to a 37-month high. The last time the growth rate was higher was during February of 2017, when the growth rate was 7.9 percent. During February 2020, year-over-year (YOY) growth in the money supply was at 7.49 percent. That's up from January's rate of 6.32 percent, and up from February 2019's rate of 3.20 percent.
Read More »
Read More »
The Fed’s Massive Injection of “Liquidity” Also Benefits Uncle Sam
There’s a lot to be said regarding the Fed’s surprise announcements—including its Sunday surprise of $700 billion in renewed QE and the complete elimination of all reserve requirements for banks—but here let me just focus on one element: the tendency for Fed officials and all the pundits to treat injections of “liquidity” as if they don’t count as much when distorting the economy.
Read More »
Read More »
Modern Monetary Theory Is an Old Marxist Idea
Modern monetary theory, or MMT, has been getting a lot of attention lately, often celebrated as a revolutionary breakthrough. However, there is absolutely nothing new about it. The very basis of the theory, the idea that governments can finance their expenditures themselves and that therefore deficits don’t matter, actually goes back to the Polish Marxist economist Michael Kalecki (1899–1970).
Read More »
Read More »
The CDC’s Budget Is Larger Now Than Under Obama
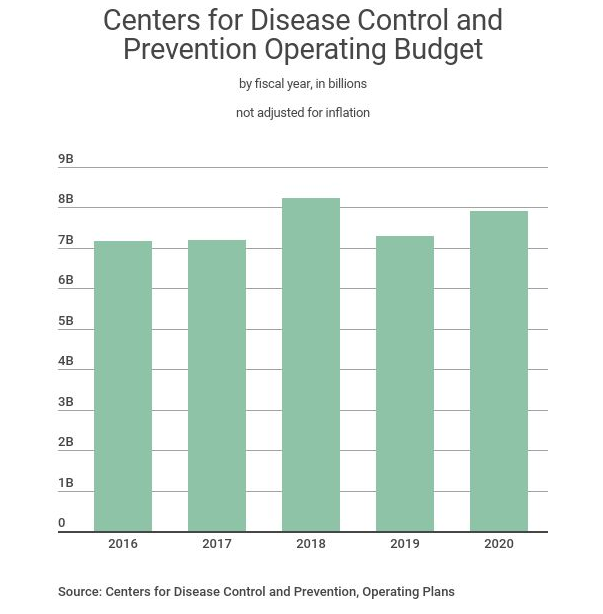
This is how the budget process in Washington begins. Step one: the president submits his budget to Congress. Step two: Congress puts the president's budget in a drawer somewhere and forgets about it. Step three: Congress passes a budget it likes instead.
Read More »
Read More »
Why Medicare for All Would Require Huge Tax Increases
Medicare for All is listed as the top priority of Democratic presidential candidate Bernie Sanders. He describes it as a single-payer system that is “free at the point of service” as there will be no premiums, deductibles, copays, or surprise bills. It will cover more services (dental, hearing, vision, long-term care, substance abuse treatment, etc.) than what the present Medicare system covers. It will also stop the “pharmaceutical industry from...
Read More »
Read More »
The “Market Monetarists” and NGDP Targeting
[This article is part of the Understanding Money Mechanics series, by Robert P. Murphy. The series will be published as a book in late 2020.] In addition to the Keynesian perspective (covered in chapter 14), a relatively new challenge to the Austrian framework comes from the “market monetarists” and their endorsement of a central bank policy of “level targeting” of nominal gross domestic product (sometimes abbreviated as NGDPLT1).
Read More »
Read More »
If China Is the Problem, Can’t We At Least Have Free Trade with Everyone Else?
It remains unclear how much the stock market implosion of recent days will affect the larger economy. As David Stockman has noted often, the Wall Street economy is not synonymous with the Main Street economy, contrary to what the advocates of rampant bank bailouts and financialization would have us believe.
Read More »
Read More »
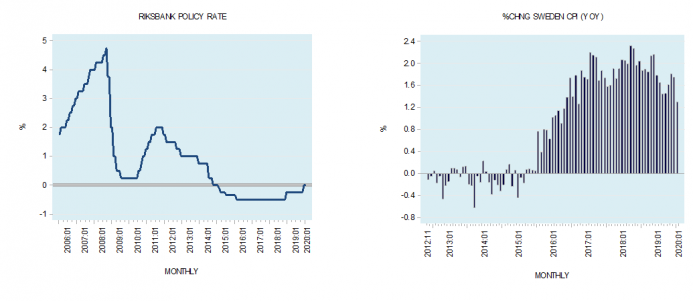
Why Sweden’s Negative Interest Rate Experiment Is a Failure
According to the Financial Times's February 20 article “Why Sweden Ditched Its Negative Rate Experiment,” economists are pondering whether Sweden’s central bank experiment with negative interest rate was a success. Sweden’s Riksbank, the world’s oldest central bank, introduced negative interest rates in early 2015.
Read More »
Read More »
What Comes After Quantitative Easing?
André de Godoy: Ludwig von Mises mentions in his books that credit expansion is one of the causes of the inflation beyond the monetary expansion. What are the similarities and differences between those two phenomena?
Read More »
Read More »
What Would Murray Say About the Coronavirus?
Murray Rothbard died in January 1995, long before this year’s coronavirus scare. But the principles this great thinker taught us can help us answer questions about the coronavirus outbreak which trouble many of us. Would the US government be justified in imposing massive involuntary quarantines in order to slow down the spread of disease? What about vaccines?
Read More »
Read More »
The US Constitution Needs an Expiration Date
A unique feature of the Swiss Federal Constitution is the fact that the central government's power to impose direct taxes on citizens expires every decade or so. In fact, the current taxing authority expires at the end of 2020. Fortunately for the Swiss republic's central government, voters approved an extension (the "New Financial Regime 2021") for another fifteen years in a March 2018 election.
Read More »
Read More »