– There has been a recent change for the better in central bank attitudes to gold
– There has been “net gold demand by central banks – approx. 500 tonnes per year – as a source of return, liquidity and diversification”
– Policy shift to maintaining stable gold holdings reflects central bank concerns about financial markets and geopolitics
– Little in the current global economic and political environment to support any reason to change in this conservative position
– Central bank positivity to gold and gold buying should provide long-term underlying support to gold prices
| Should central banks hold gold?
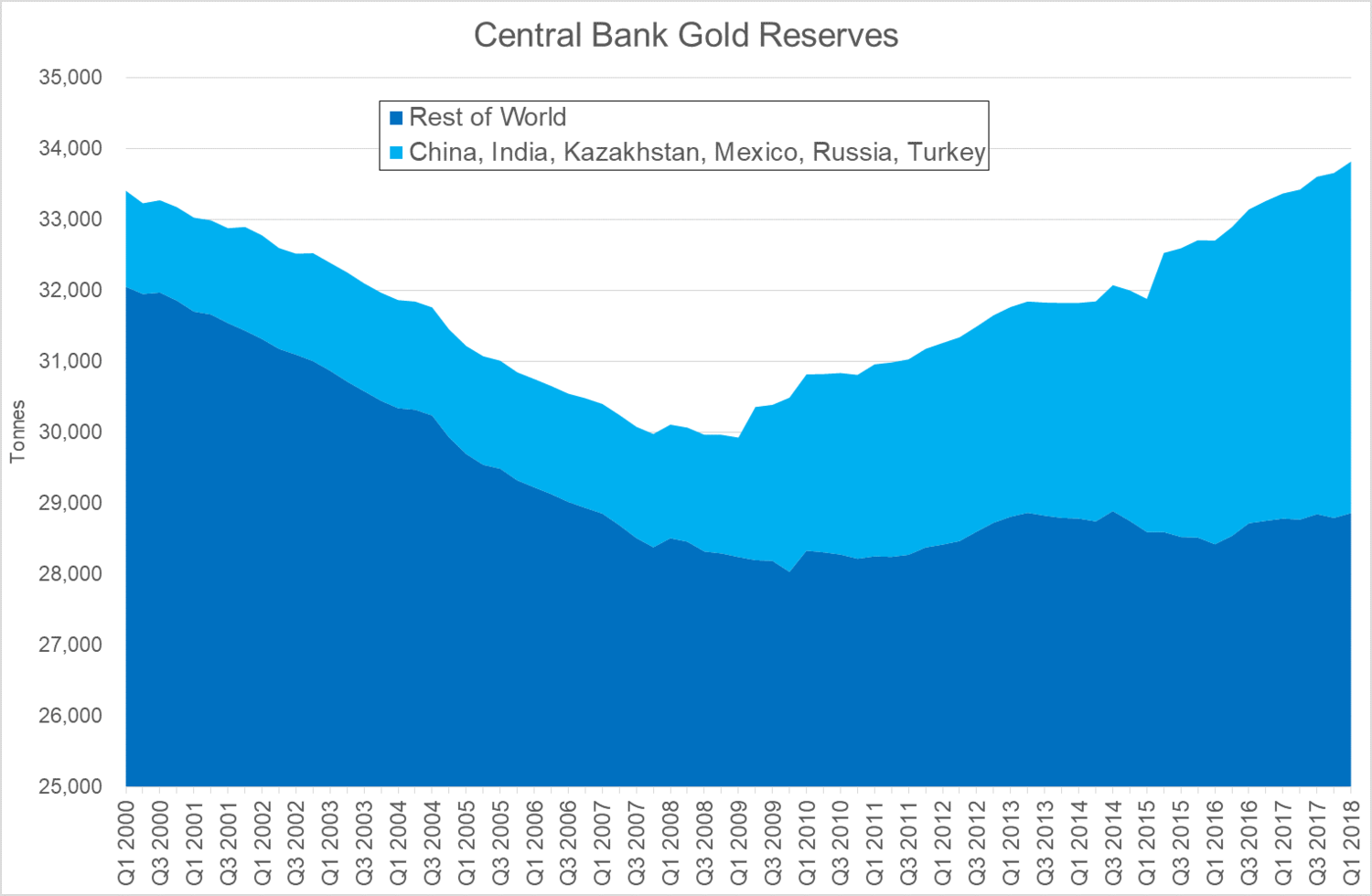
From the late 1980s into the new millennium the answer appeared to be in the negative, with global central bank reserves declining from around 36,000 tonnes to under 30,000 tonnes. Decades of consistent central bank gold sales were so detrimental to gold market sentiment that in 1999, as gold was selling off towards sub-$250 per ounce, fourteen central banks agreed to limit their selling under the Washington Agreement on Gold. Soon after, gold began its bull market run to over $1,900 although central banks continued to sell, on average, 400 tonnes a year. Today, at close to 34,000 tonnes, total central bank gold reserves have recovered to a 20-year high, primarily driven by China and Russia and other emerging market countries. A focus on the aggregate figure, however, hides a more fundamental change in central bank attitudes towards gold that occurred after the late 2008 financial crisis, when central bank reserves bottomed. This chart groups the six central banks who have increased their gold reserves by more than 100 tonnes since the 2008 financial crisis, compared to the remaining central banks. Excluding the key gold accumulating countries of China, India, Kazakhstan, Mexico, Russia and Turkey, the gold holdings of other central banks has been stable since the global financial crisis, a timing which is unlikely to be coincidental. The chart also shows that that while central bank gold reserves in total are now back to where they were in 1999, almost all of the increase was due to six central banks. As the World Gold Council notes, “the expansion of EM foreign reserves has resulted in net gold demand by central banks – approx. 500 tonnes per year – as a source of return, liquidity and diversification”, with many commentators interpreting it as a strategic diversification by China and Russia away from the US dollar. |
Central Bank Gold Reserves, Q1 2000 - Q1 2018 |
| This is a major structural change in global central bank attitudes towards gold after decades of selling.
Clearly the policy shift to maintaining stable gold holdings reflects broad central bank concerns about financial markets and geopolitics. With little in the current global economic and political environment to support any reason to change in this conservative position, it should provide long-term underlying support to gold prices. Courtesy of the Gold Industry Group |
 |
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next post
Tags: Daily Market Update,newsletter