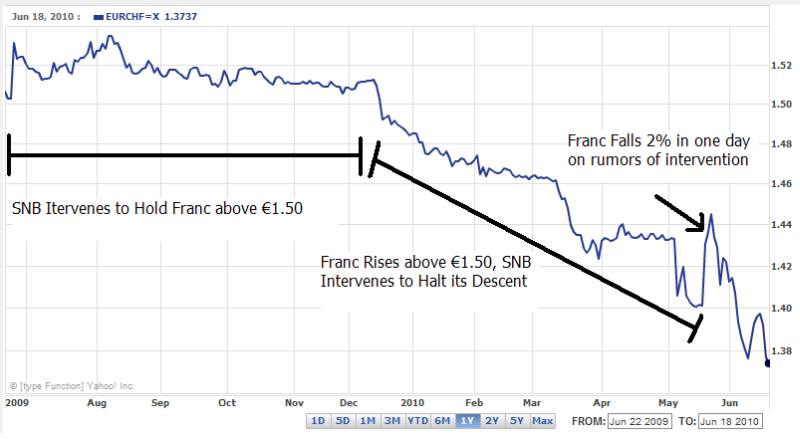
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) has apparently admitted (temporary) defeat in its battle to hold down the value of the Franc. ” ‘The SNB has reached its limits and if the market wants to see a franc at 1.35 versus the euro, they won’t be able to stop it.’ ” The markets have won.The SNB has lost.
Still, the SNB should be applauded for its efforts. As you can see from the chart above, it managed to keep the Franc from rising above €1.50 (its so-called line in the sand) for the better part of 2009. Furthermore, by most accounts, it managed to slow the Franc’s unavoidable descent against the Euro in 2010. While the Dollar has appreciated more than 15% against the Euro, the Franc has a risen by a more modest 10%. ” ‘Without that €90 billion [intervention], it’s fair to say that the euro would be closer to $1.10,’ ” argued one analyst. In fact, as recently as May 18, the SNB manifested its power in the form of 1-day, 2% decline in the Franc, its sharpest fall in more than a year.
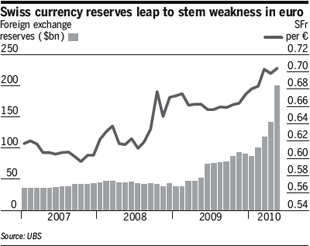
Overall, the SNB has spent more than $200 Billion over the last 12 months, including $73 Billion in the month of May alone. ” ‘To put the figures in perspective, there have been only two months when China, the world’s largest holder of forex reserves with $2,249bn in assets, saw its reserves increase more.’ ” The SNB now claims the world’s 7th largest foreign exchange reserves, ahead of the perennial interveners of Brazil in Hong Kong, the latter of whose currency is pegged against the Dollar.
While the SNB can take some credit for halting the decline in the Franc, it was ultimately done in by factors beyond its control, namely the Eurozone sovereign debt crisis and consequent surge in risk aversion. At this point the forces that the SNB is battling against are too large to be contained: “We’re talking about a massive euro crisis, so no single central bank can prop it up on its own,” summarized one trader. As a result, the Franc is now rising to a fresh record high against the Euro nearly every trading session.
Still, the SNB remains committed to rhetorical intervention. “The central bank has a ‘clear aim‘ to maintain price stability and this is what guides its policy actions, SNB President Philipp Hildebrand said…The bank will act in a ‘decisive manner if needed.’ ” That means that if economic growth slows and/or deflation sets it, it may have to restart the printing presses. Given that its economy is slated to grow at a solid 1.5% this year, unemployment is a meager 3.8%, and the threat of inflation has largely abated. On the other hand, the prospect of a drawn-out crisis in the EU means the Franc will probably continue to appreciate – without help from the Central Bank: ” ‘The SNB may continue to intervene in the currency markets until 2020,’ ” declared the head of forex research for UBS.
The implications for currency markets are interesting. Not only has the SNB prevented the Euro from falling too fast against the Franc, but it may also have prevented it from falling too quickly against other currencies. ” ‘To suggest that the SNB has been the savior of the euro is too much. But one could imagine that if the euro starts to decline again, the market may blame the fact that the SNB isn’t buying,’ ” said a currency strategist from Standard Bank.
This episode is also a testament to the limits of intervention. It has always been clear (to this blogger, at least) that intervention is futile in the long-term. The best that a Central Bank can hope for is to stall a particular outcome long enough in order to achieve a certain short-term policy aim. When enough momentum coalesces behind a (floating) currency, there is nothing that a Central Bank can do to stop it from moving to the rate that investors collectively deem it to be worth.
Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next post
Tags: Euro crisis,franc,intervention,Swiss National Bank,Switzerland