Swiss National Bank (SNB) Policy Update
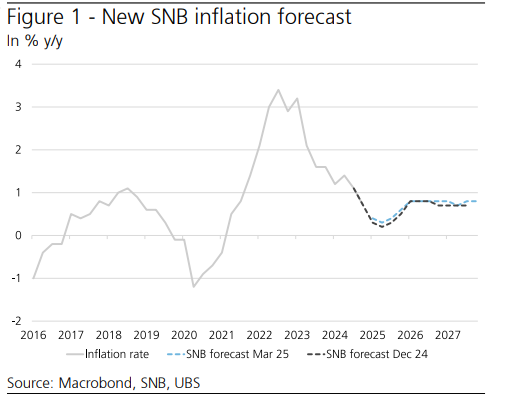
Policy Rate Cut: SNB lowered its policy rate from 0.50% to 0.25% due to low inflationary pressure and rising downside risks.
2025 Outlook: The policy rate is expected to remain at 0.25% for the rest of the year.
Economic Outlook
UBS Main Scenario:
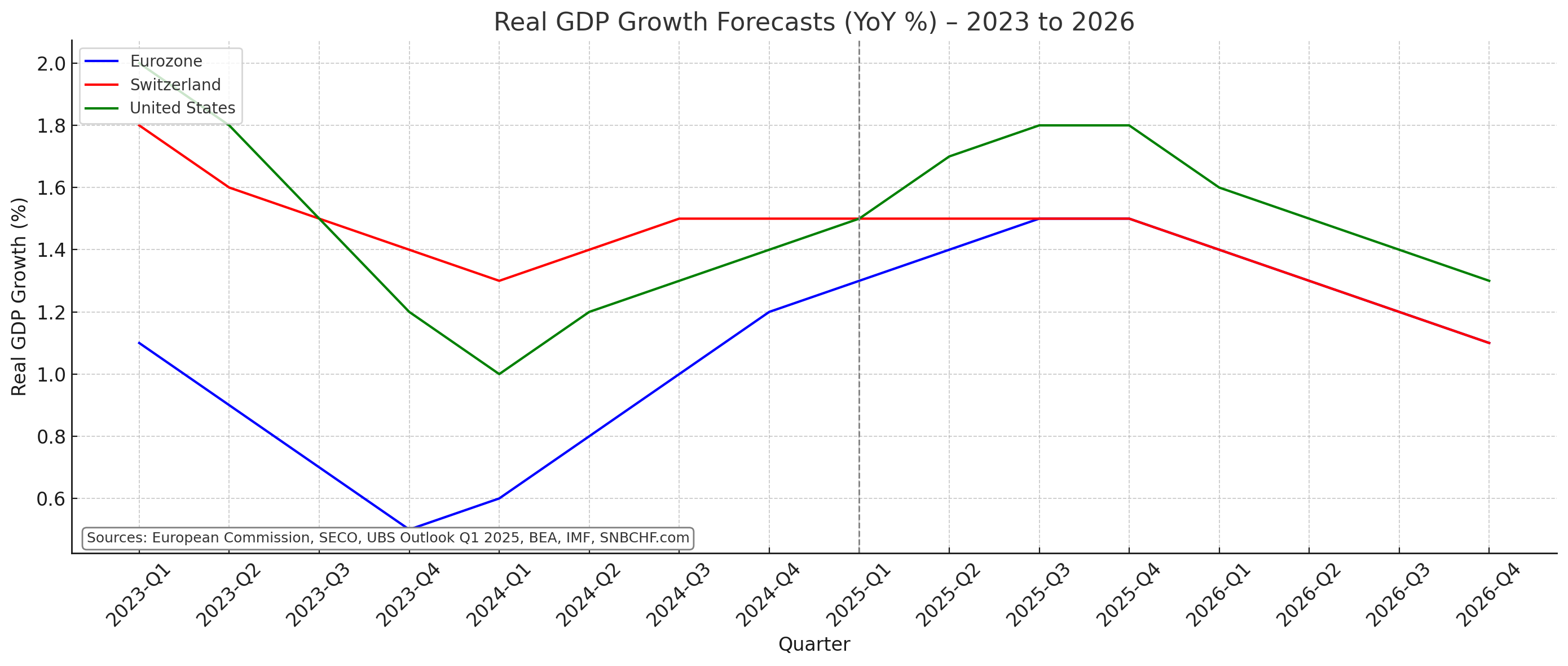
Swiss GDP growth around 1.5%, slightly above SNB’s forecast.
Inflation to stay below 0.5% in H1, then rise modestly.
Stable Swiss franc expected.
Downside Risk:
A global tariff shock could harm EU and Swiss growth.
Potential appreciation of the Swiss franc.
SNB might cut rates further and intervene in FX markets.
Upside Risk:
If EU-US trade tensions ease and Germany loosens fiscal policy, inflation could rise.
SNB may eventually need to raise rates, but this is unlikely before 2026.
Comment by George Dorgan:
It is visible that Switzerland GDP growth is higher than the one in the European Union, already since 2023.
Sources:
Currency Forecasts
UBS predicts:
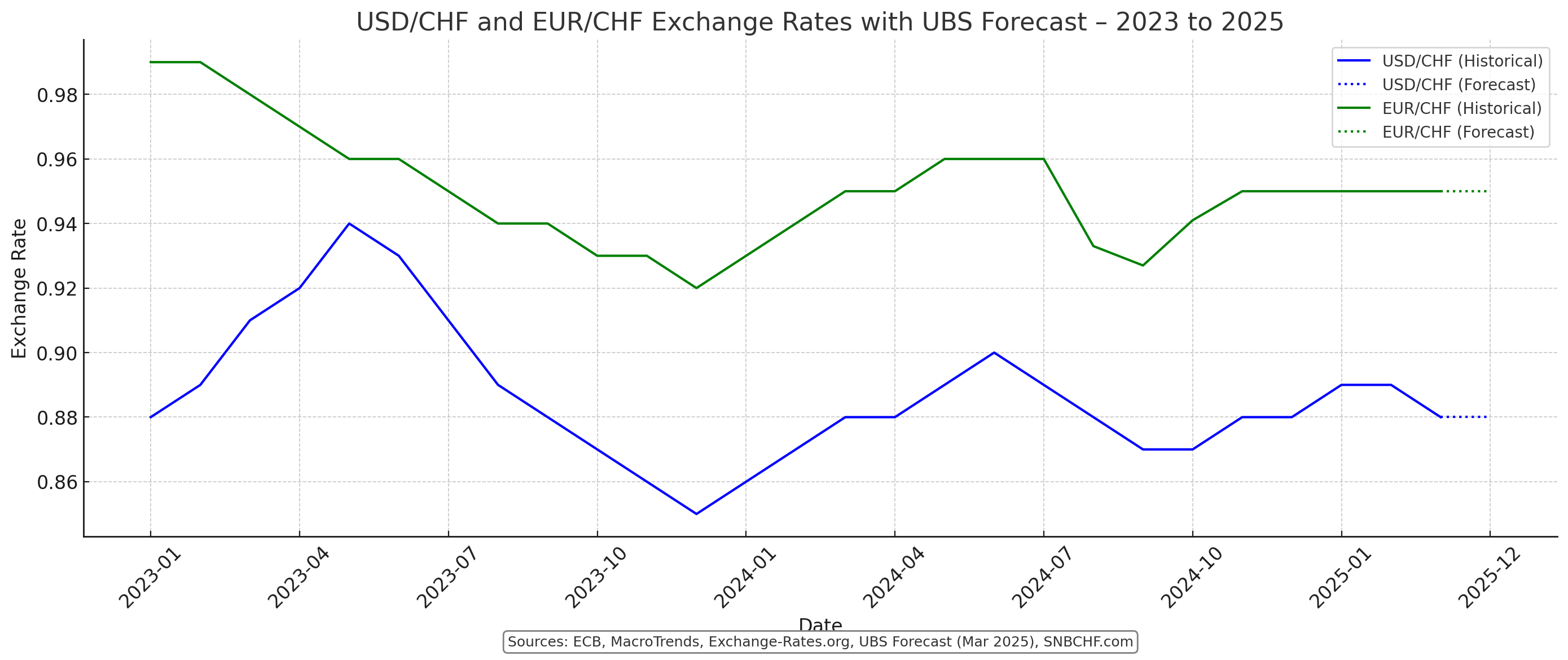
EUR/CHF: Expected to hover around 0.95.
USD/CHF: Forecast at 0.85 over 12 months.
Comment by George Dorgan:
UBS completely ignores the fact that Swiss inflation is lower than the one in EU.
By the interest rates parity , the Swiss franc must rise, unless the ECB keeps higher rates for longer (as the U.S. does).
Morover as stated above, higher Swiss GDP growth usually entails higher yields on Swiss investments and therefore a higher CHF.
Forex brokers in Switzerland
Sources:
Bond Yields
UBS states:
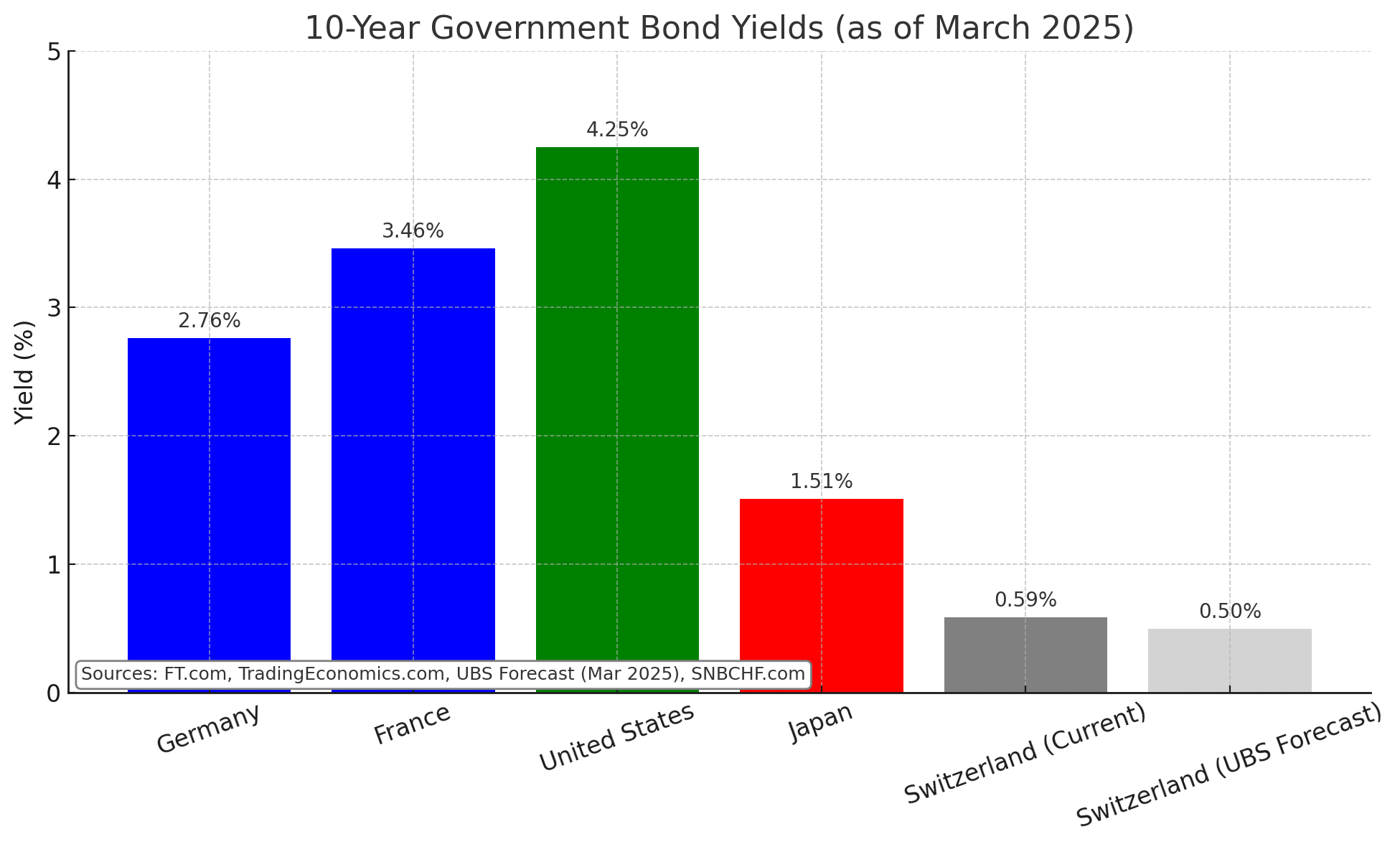
10-year Swiss yield forecast revised slightly higher from 0.3% to 0.5%.
Still downside risk due to geopolitical and trade tensions.
Comment by George Dorgan:
The massive yield differential between the U.S. and Switzerland opens the possibility for a carry trade.
Beware that carry trades often collapse, the reverse carry trade.
Question is still if the USD will loose 4% in value against CHF per year.
Sources:
Mortgage Market Impact
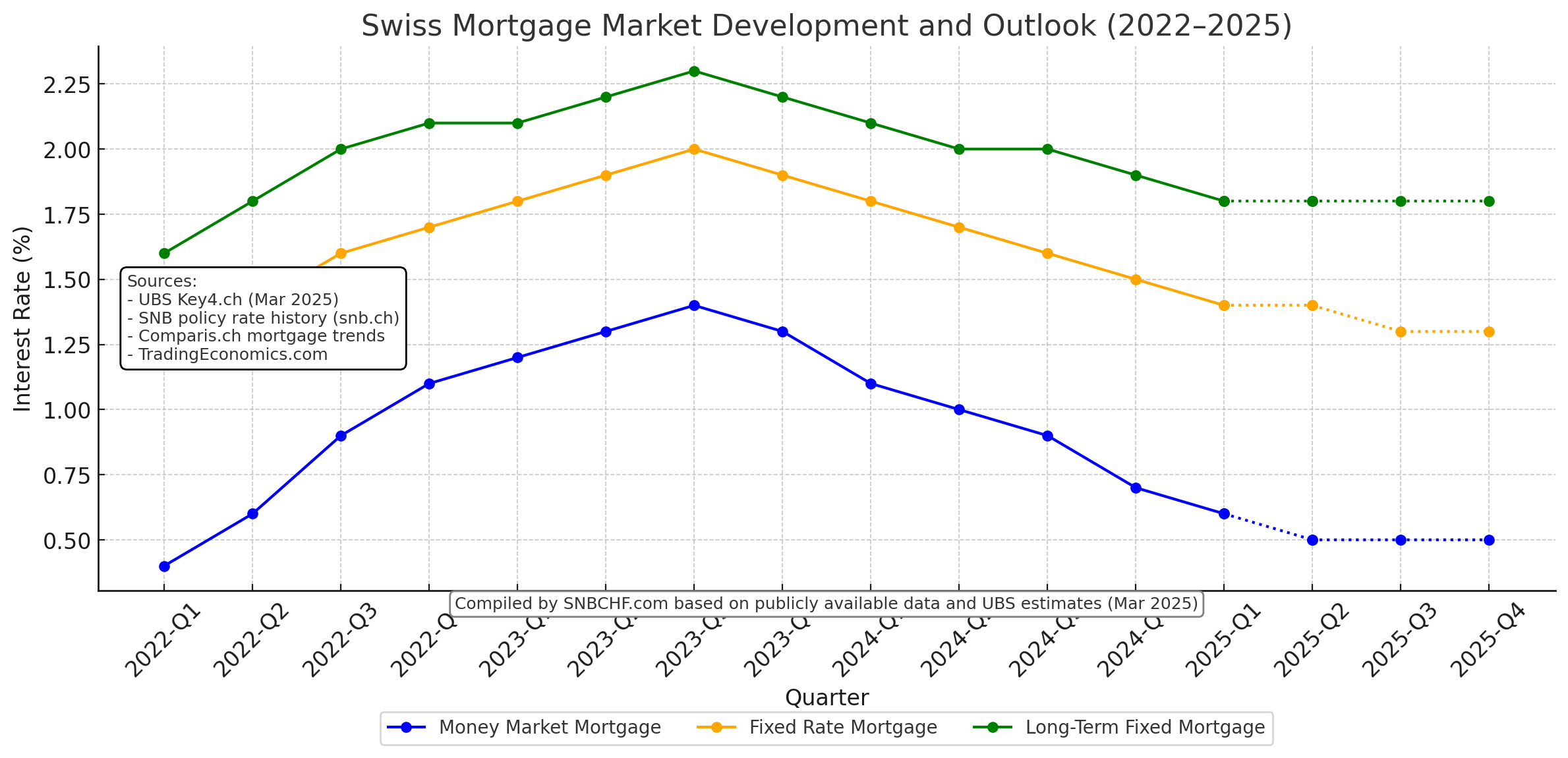
Money-market mortgage rates are falling.
Fixed-rate mortgages may become slightly cheaper.
Long-term fixed mortgages remain attractive as a hedge against potential inflation and rate increases.
Sources:
Tags: