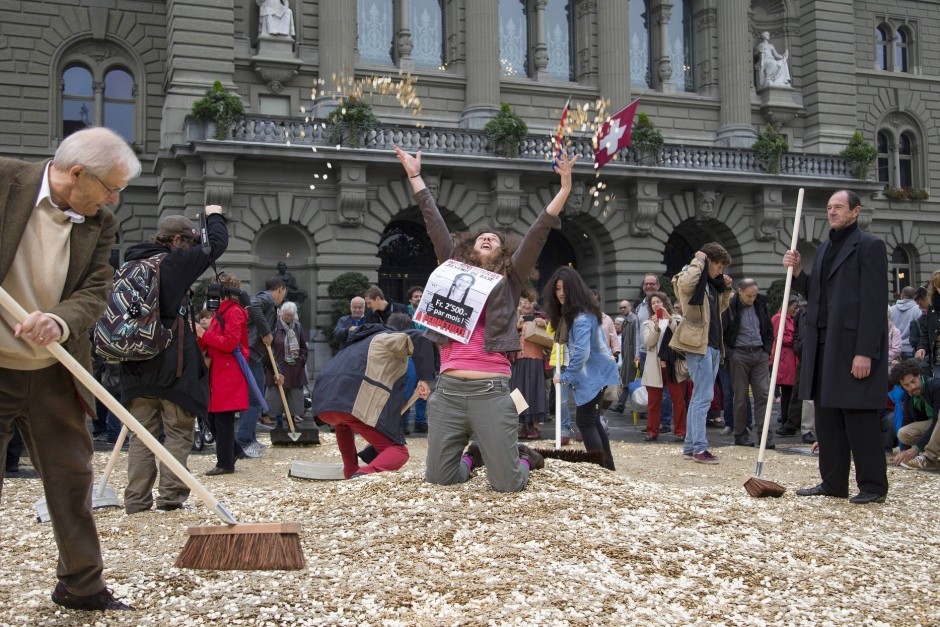
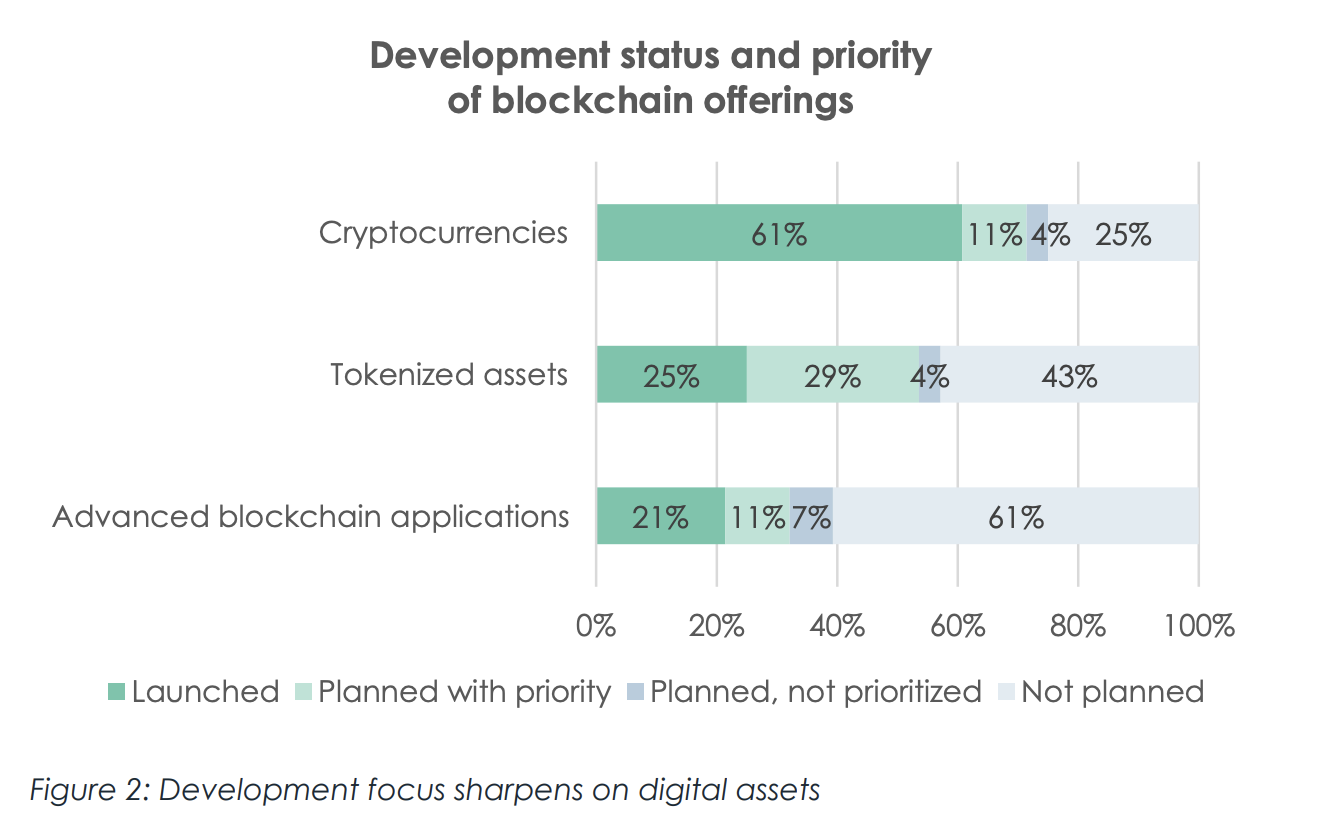
This weekend the Swiss population was called upon to make a historic decision, when Switzerland became the first country worldwide to put the idea of free money for everyone, technically known as Unconditional Basic Income (of CHF2,500 per month for every adult). The Swiss rejected the proposal with a big majority. - Click to enlarge
This weekend the Swiss population was called upon to make a historic decision, when Switzerland became the first country worldwide to put the idea of free money for everyone, technically known as Unconditional Basic Income (of CHF2,500 per month for every adult man and woman, and CHF625 for every child, for doing absolutely nothing) to a vote.
As reported previously, the outcome of this referendum would set a strong precedent and establish a landmark in the evolution of the debate of handing out free money in a centrally-planned world. And as predicted, based on early vote projections it has been a landslide decision against the “free lunch.”
According to BBC, some 78% of voters opposed the plan, a GFS projection for Swiss TV suggested. AFP adds that most Swiss vote in advance by post, so a large majority of ballots had already been counted, and gfs.bern put the margin of error at just plus/minus three percent.
Supporters said since work was increasingly automated, fewer jobs were available for workers. Switzerland is the first country to hold such a vote. No figure for the basic income had been set, but those behind the proposal suggested a monthly income of 2,500 Swiss francs (£1,755; $2,555) for adults and SFr625 for each child, reflecting the high cost of living in Switzerland. It is not clear how it would affect people on higher salaries.

This weekend the Swiss population was called upon to make a historic decision, when Switzerland became the first country worldwide to put the idea of free money for everyone, technically known as Unconditional Basic Income (of CHF2,500 per month for every adult). The Swiss rejected the proposal with a big majority. - Click to enlarge
“We are very happy,” Ralph Kundig, one of the lead campaigners, told the ATS news agency. Supporters threw a party in Lausanne to celebrate the 22 percent of votes they had garnered. “One out of five people voted for the unconditional basic income, so that is a success in itself,” Sergio Rossi, an economics professor and backer of the initiative, told ATS.
However, there was little support among Swiss politicians for the idea and not a single parliamentary party has come out in favour, but the proposal gathered more than 100,000 signatures and was therefore put to the vote under the Swiss popular initiative system.
Critics of the measure say that disconnecting the link between work done and money earned would be bad for society. But Che Wagner from the campaign group Basic Income Switzerland, says it wouldn’t be money for nothing. “In Switzerland over 50% of total work that is done is unpaid. It’s care work, it’s at home, it’s in different communities, so that work would be more valued with a basic income.”
Luzi Stamm, who’s a member of parliament for the right-wing Swiss People’s Party, opposes the idea. “Theoretically, if Switzerland were an island, the answer is yes. But with open borders, it’s a total impossibility, especially for Switzerland, with a high living standard,” he says.
“If you would offer every individual a Swiss amount of money, you would have billions of people who would try to move into Switzerland.”
Because, one you start handing out free lunches, everyone wants a piece of the pie…
Andreas Ladner, a political scientist at Lausanne University, told RTS the Swiss were “realistic” in their assessment of the UBI plan. Accepting that people can “be paid without having to work would have been a very big step” for the industrious Swiss, he said.
Critics have slammed the initiative as “a Marxist dream”, warning of sky-high costs and people quitting their jobs in droves, causing economic chaos.
The wording on the initiative was vague, asking for a constitutional change to “guarantee the introduction of an unconditional basic income” but with no mention of amounts.
Switzerland may be the first but it won’t be the last. The idea is also under consideration elsewhere. In Finland, the government is considering a trial to give basic income to about 8,000 people from low-income groups. And in the Dutch city of Utrecht is also developing a pilot project which will begin in January 2017.
* * *
Meanwhile, here are some recent thoughts on why the idea of a Free Lunch, old as time, will never work.
The Free Lunch – A Fantasy as Old as Methuselah
The promise of a free lunch is by no means a new thing in politics. Getting “something for nothing” is an age-old shiny trinket that has been dangled before the eyes of the public since time immemorial. In fact, it has appeared so excruciatingly often in our political history, for centuries on end, that one would think that it wouldn’t work anymore; not in 2016, surely. And yet it does. UBI is the proof that there are still people who choose to believe that “no strings attached” freebies and gifts are promises one can rely on and build an economy on, especially when they are coming from their government and rulers.
However, there are always some strings attached to such gifts and if history has taught us anything on this matter, it is the distinction between a gift and a bribe. Unsavory political ideologies and catastrophic cultural philosophies often tend to make their debut in front of the public hidden inside a Trojan gift horse. Unrealistic yet enchanting promises have always been a reliable political tool and it has never been a big strategic challenge to corrupt the people by granting the majority something that was stolen from minorities.
The Cultural Argument for Collectivism
Key figures of the pro-UBI camp take pride in claiming that the main motivation behind the campaign is not economic but cultural. They say this proposal aims to make people think about the nature of life and work, it is a way to liberate them from the jobs they don’t like but need, a status which the scheme’s advocates, quite unhistorically, equate to the indignity of slavery. On top of this, they claim, UBI will help society survive the imminent unemployment apocalypse: they believe that with the help of automation and artificial intelligence 50% of all the existing jobs will be taken over within the coming decade by computers and machines.
Such an argument might sound superficially rational, but it goes deeper than that: It presupposes that we as human beings see ourselves downgraded and equated to a machine, like just another cog that can be replaced at any time, in a system where man is literally defined as a human resource.
The truth is that it is indeed a cultural debate, far more than it is an economic one. The only conceivable aim of such a factually unhinged and unfounded proposal can be to gauge the mind-set of the Swiss people in this moment in time. The outcome of this referendum can provide a valuable insight into the Swiss mentality, and whether the Swiss actually prefer collectivism over individualism. Such a signal could serve as cue for a further escalation of government empowerment: After all, the collapsing centralized system is bound to show symptoms of desperation by “doubling down” and accelerating and maximizing its centralization efforts. Thus focusing on the symptoms and secondary effects is futile; a real difference can only be made by addressing the root cause, the system itself.
Despite the economic non-sequiturs and the plain Utopianism that lie at the core of the idea of a Universal Basic Income, the concept seems to be gaining popularity worldwide. Canada is set to conduct an experiment with this idea later this year. The city of Utrecht in the Netherlands is launching a pilot program, Finland is planning a two-year trial and a British proposal is gathering interest, while the nonprofit group Give Directly will start providing a guaranteed income to 6,000 Kenyans this month in a decade-long scheduled program and track the results. The idea seems to be gaining traction due to the Western Left’s efforts, however the polls in Switzerland are painting a dramatically different picture: the UBI initiative is projected to suffer a crushing defeat.
A Bastion of Liberty
The Swiss have been voting counter-intuitively for years: When they held a referendum for or against six weeks of vacation, or when they were called upon to vote for an initiative advocating fewer working hours, or even when they made their choice on the issue of the minimum wage, they always delivered outcomes that seemed surprising to the rest of the West, especially the rest of Europe. Up to now, the Swiss have consistently rejected interference by the state when it came to such topics and have refused to grant more powers to their government. Even in recent years, when the trend in favor of aggressive state expansionism seems to be stronger than ever, Switzerland appears to still hold the line as the last bastion of liberty that remains standing.
So what is so different about the Swiss then? Switzerland is indeed very different, because it became a nation by its peoples’ own will, based on limited government, strong private property rights and a direct democracy founded on the principles of subsidiarity. This has always required open dialogue and being exposed to different ideas and values: Vigorous debate itself leads to an enlightened society. Thus, the essential difference lies in the nation’s culture, mentality and philosophy.
The Swiss have grown up in an environment in which the people were always able to decide for themselves, but they also have a long tradition of doubt and of dissent. Every critical issue is discussed and decided by the people, the actions of government are subject to the judgment of and limited by the citizenry. All viewpoints are heard, even anti-establishment voices have their say, and critical thinking provides the basis for society’s future. However, this is only possible when people rely on their own mind to think about the issues individually and independently.
Switzerland is therefore quite a hostile terrain for those who wish to promote “free lunches” and “no strings attached” gifts. A long history of independent thinking, of consequential analysis and of government limitation, makes it very easy for the Swiss to see past the populism-fueled empty promises and the associated publicity stunts. The upcoming rejection of the UBI proposal on June the 5th will and should serve as a reminder that the Swiss still remain the exception to the rule.
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next postTags: Finland,Netherlands,newslettersent,Switzerland,Unemployment