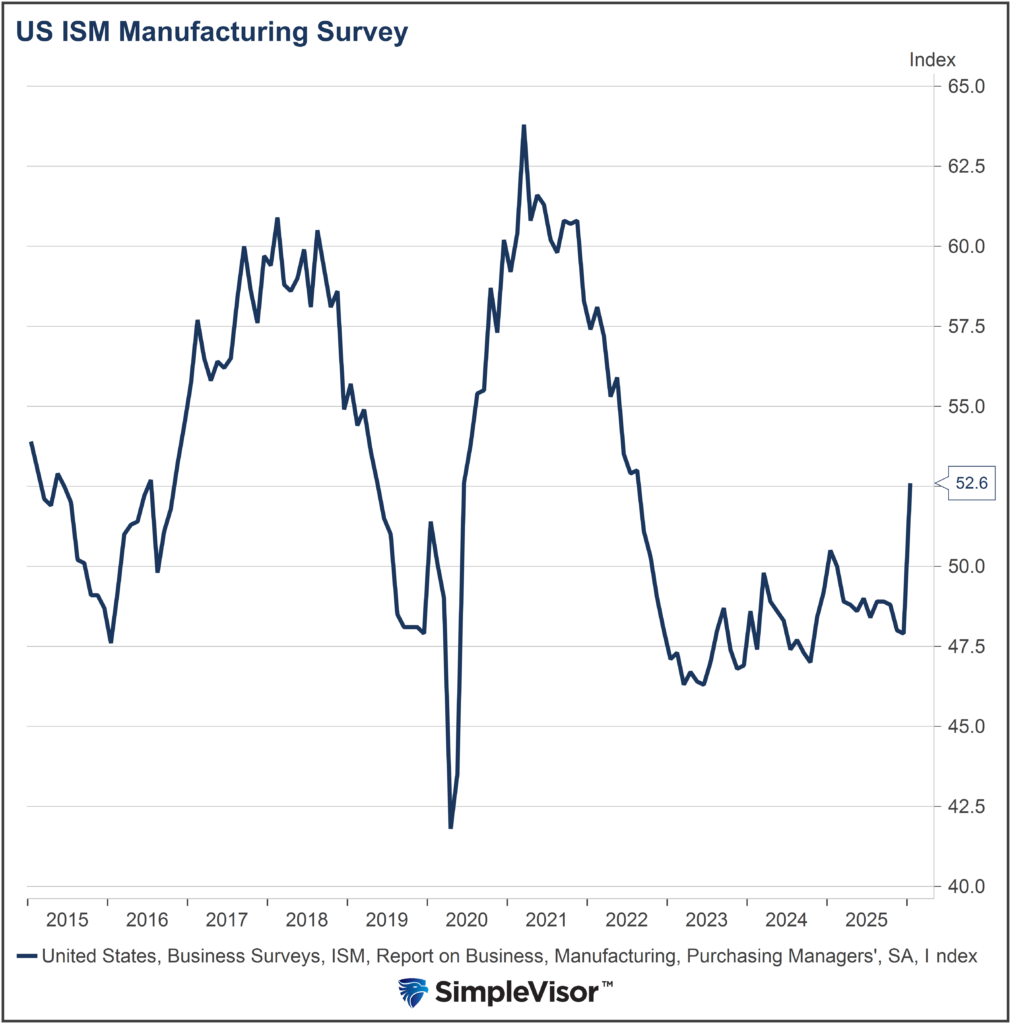
The global economy is way past the point of maximum debt saturation, and so the next stop is debt exhaustion.
Just as generals fight the last war, central banks always fight the last financial crisis. The Global Financial Crisis (GFC) of 2008-09 was primarily one of liquidity as markets froze up as a result of the collapse of the highly leveraged subprime mortgage sector that had commoditized fraud (hat tip to Manoj S.) via liar loans and designed-to-implode mortgage backed securities.
The central bank “solution” to institutionalized, commoditized fraud was to lower interest rates to zero and enable tens of trillions in new debt. As a result, total debt in the U.S. has soared to $70 trillion, roughly 3.5 times GDP, and global debt has skyrocketed from $84 trillion to $250 trillion. Debt in China has blasted from $7 trillion 2008 to $40 trillion in 2018.
A funny thing happens when you depend on borrowing from the future (debt) to fund growth today: the new debt no longer boosts growth, as the returns on additional debt are increasingly marginal. This leads to what I term debt exhaustion: lenders can no longer find creditworthy borrowers, borrowers either don’t want more debt or can’t afford more debt, and the cost and risk of the additional debt far outweigh the meager gains. Whatever credit is issued is gambled in speculations that the current bubble du jour will continue indefinitely.
Unfortunately, all central banks know how to do is goose liquidity to inflate asset bubbles and juice the issuance of more debt. If asset bubbles start to deflate, then central banks start buying mortgages, empty flats, stocks and bonds to prop up markets that would otherwise implode.
| Equally unfortunately, propping up asset bubbles and stimulating more debt to chase speculative gambles only increases the fragility of the asset bubbles and the economy that has come to rely on them for “growth”. A useful concept here is debt saturation: just as an absorbent material can only hold so much water, a corporation, household or economy can only support so much debt before servicing the debt reduces income and increases the risk of default.
The global economy is way past the point of maximum debt saturation, and so the next stop is debt exhaustion: a sharp increase in defaults, a rapid decline in demand for more debt, a collapse in asset bubbles that depend on debt and a resulting drop in economic activity, a.k.a. a deep and profound recession that cannot be “fixed” by lowering interest rates or juicing the creation of more debt. |
Debt Securities and Loans 1960-2018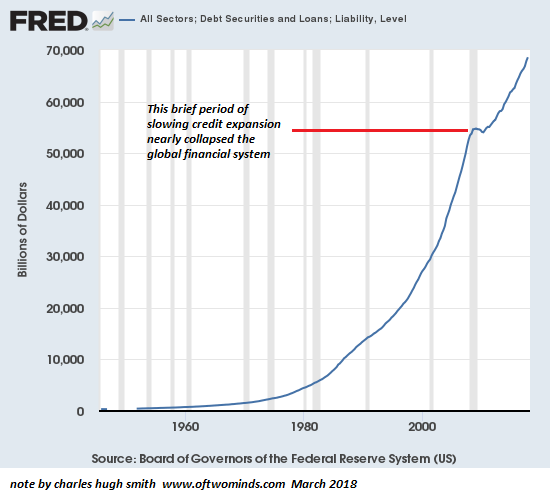 - Click to enlarge |
My new book is The Adventures of the Consulting Philosopher: The Disappearance of Drake. For more, please visit the
book's website.
Full story here
Are you the author?
At readers' request, I've prepared a biography. I am not confident this is the right length or has the desired information; the whole project veers uncomfortably close to PR. On the other hand, who wants to read a boring bio? I am reminded of the "Peanuts" comic character Lucy, who once issued this terse biographical summary: "A man was born, he lived, he died." All undoubtedly true, but somewhat lacking in narrative.
Previous post
See more for 5.) Charles Hugh Smith
Next post
Tags:
newsletter