Tag Archive: Target2
“It’s A Perfect Storm Of Negativity” – Veteran Trader Rejoins The Dark Side
After many months of fighting all the naysayers predicting the next big stock market crash, I am finally succumbing to the seductive story of the dark side, and getting negative on equities. I am often early, so maybe this means the rally is about to accelerate to the upside.
Read More »
Read More »
Italian Euro Exit: Why it Might Come in some Years and Why it Will Help the Euro Zone and Italy
Italy has three options: 1. exit the euro zone and devalue the currency; 2. remain in the euro zone and devalue salaries. 3. go for Japan-like decades-long slow growth with stagnating wages, but also with falling inflation and (positive news!) falling bond yields.
Read More »
Read More »
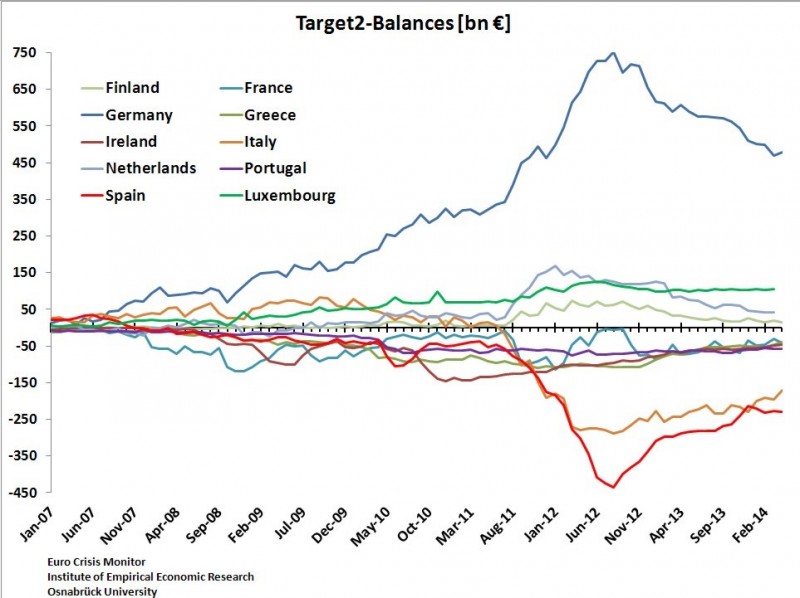
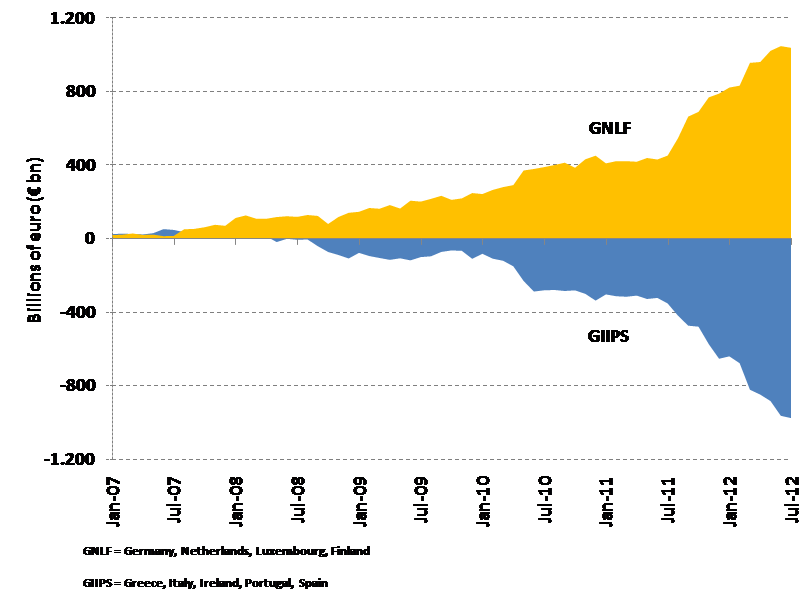
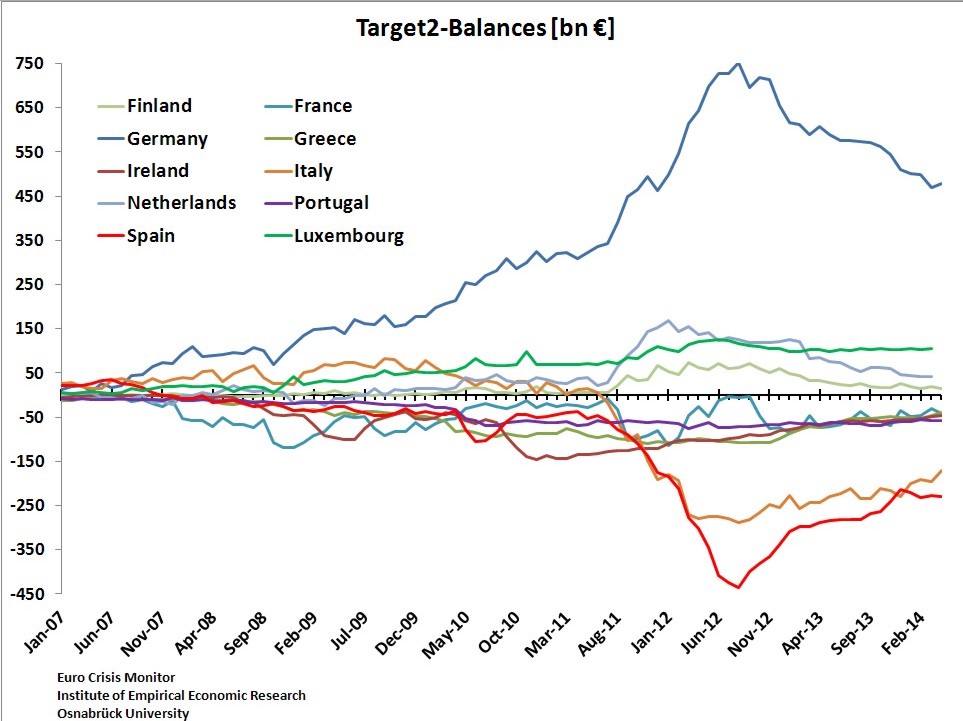
L’Allemagne est le patron-sponsor de l’Eurosystem.
Lors des échanges commerciaux et interbancaires, il y a des banques émettrices de monnaie et vis-à-vis une banque réceptrice. Normalement, à la fin de la journée, tout cela devrait être ramené à l’équilibre. Ceci n’est plus le cas depuis la crise américaine de 2007 (subprimes) comme nous le voyons sur le graphique ci-dessous de quelques pays de la zone euro.
Read More »
Read More »
Negative Rates for Bundesbank TARGET2 Surplus?
The ECB surprised with negative rates on excess reserves, on the deposit facility and even on TARGET2. We clarify whether the Bundesbank, as a member of the euro system, must pay negative interest rates on its huge TARGET2 surplus.
Read More »
Read More »
Germany: Last European Country with Lots of Cash Under Matresses
In June 2014, the ECB decided to introduce negative rates on the excess reserves of banks. We explain that German banks had already removed most excess liquidity before the ECB meeting of June 2014, and they will continue to do so. Hence hardly any German bank will pay negative rates after the recent ECB decisions at that meeting.
Read More »
Read More »
Why negative interest rates are contractionary, the base money confusion
From FT Alphaville: Excess reserves do not mean banks are not lending, and enforcing negative rates may do more harm than good because it is ultimately contractionary rather than expansionary.
Read More »
Read More »
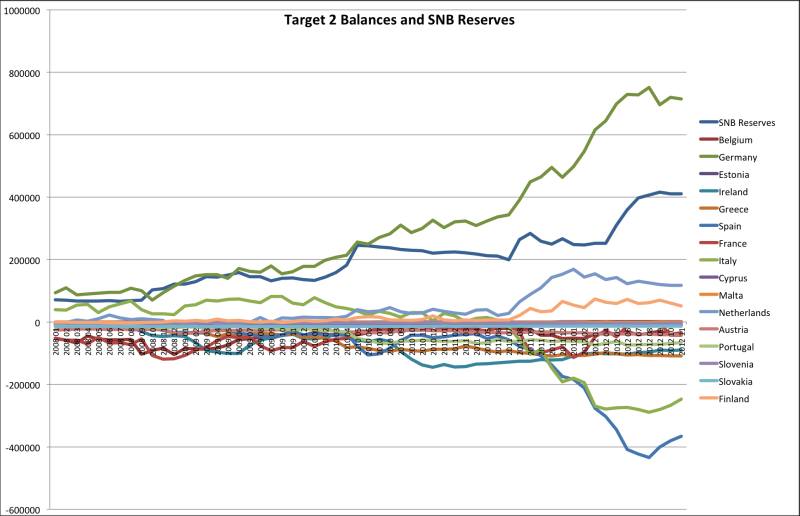
Target2 Balances and SNB Currency Reserves: Same Concept, Update February 2013
We show that Target2 imbalances and the SNB currency reserves represent the same issues, namely current account surpluses/deficits and capital flight. Therefore it makes sense to compare them, in total and by inhabitant.
Read More »
Read More »
Bad News for SNB: While Target2 Imbalances Diminish, SNB Reserves Remain the Same
As we explain here, , Target2 balances and SNB currency reserves represent the same concept, namely capital flight (in a positive and negative sense) and current account imbalances. While Target2 numbers for Germany and Northern Europe go down, SNB reserves remain the same, only 3 billion CHF away from record highs.
Read More »
Read More »
Target2 Balances and SNB Currency Reserves. They are Both the Same Concept
We show that Target2 imbalances and the SNB currency reserves represent the same issues, namely current account surpluses/deficits and capital flight. Therefore it makes sense to compare them, in total and by inhabitant.
Read More »
Read More »
German Currency and Gold Reserves and the German Trade Surplus
During the Bretton Woods system, Germany managed to obtain current account surpluses. They converted these surpluses into gold. At the time they bought it at 35$ per ounce at a relatively cheap price – at the end of the 1960s the price was augmented to 42$. At the end of the 1960 and with …
Read More »
Read More »
The Big Swiss Faustian Bargain: Differences between SNB, ECB and Fed Money Printing Explained
Potential losses due to money printing are for the Fed: 1.2% of GDP, Bundesbank: 5% of GDP, SNB: 12% of GDP.
Read More »
Read More »
The Big Swiss Faustian Bargain: Differences between SNB, ECB and Fed Money Printing Explained
In this post we show that the risks the Fed, the ECB and the Bundesbank incur are far smaller than the one the Swiss SNB takes. The Fed has “just” an inflation risk, that could cost 200 billion US$, 1.2% of US GDP. The ECB and Bundesbank have the risk that the euro zone splits … Continue reading »
Read More »
Read More »
German constitutional court needs 3 months to decide about the injunction
The German constitutional court will need up to 3 months for the injunction. Weidmann's critic on the ESM in detail. Estimations of German liability between 900 bln. and 2 trillion EUR.
Read More »
Read More »
The Northern Euro introduction: A retrospective from the year 2030
A retrospective from the year 2030 on two decades of failed european integration policy and 10 years of successful disintegration policy The following essay shows that currency regimes come and go over the time. Nothing is stable with the time, especially the use of a currency. What has never happened in history is the use …
Read More »
Read More »