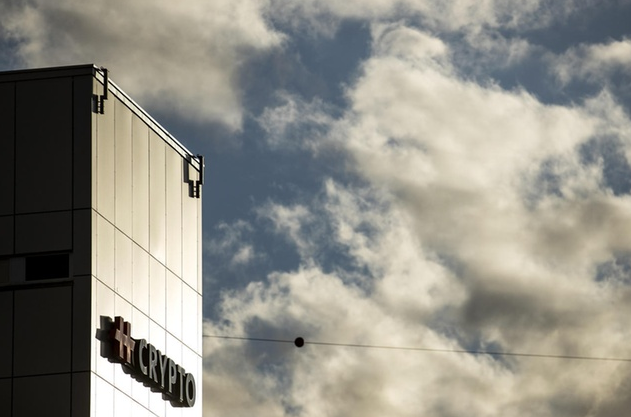
Crypto AG’s encryption machines, sold worldwide, were reportedly bugged to enable spying by the CIA and West Germany. (Keystone / Alexandra Wey)
The Swiss parliament has insisted that it will take control of and merge the ongoing investigations into the Crypto spying affair that has rocked the Alpine nation.
On Wednesday, members of the parliamentary control delegation decided to immediately take over the direction of investigation launched by the Federal Council (executive branch) on February 11.
The government had commissioned former federal judge Niklaus Oberholzer to lead the federal probe, which is expected to deliver a comprehensive report on the spying affair by June.
On February 13, the parliamentary control delegation also launched its own parallel investigation into the matter to try to find out how much the authorities knew. This investigation has already carried out four sessions with interviews; others are planned.
“In order to establish the facts quickly and efficiently, the commission has therefore decided to take over the investigation entrusted to former Federal Judge Niklaus Oberholzer,” it said in a statement on Wednesdayexternal link.
+ Why the ex-judge investigating doesn’t have open access to the files
When the affair came to light there were also calls for a parliamentary commission of inquiry – which has only ever taken place four times in Swiss history, most recently in 1996.
The Swiss authorities opened investigations into the decades-old spying affair involving Swiss firm Crypto following reports by Swiss public broadcaster SRF, German broadcaster ZDF and The Washington Post.
Their reports were based on a 280-page secret service dossier by the CIA and the German Federal Intelligence Service (BND) that showed that for decades, there had been espionage via manipulated encryption devices from the Swiss company Crypto AG. More than 100 countries bought the encryption devices from the Zug-based company, which did business under the guise of Swiss neutrality, but in reality, belonged to the CIA and the BND.
The spying allegedly continued until at least 2018, and over 100 countries worldwide were targeted.
Crypto reportedly had two types of encryption products: one fully secured, the other non-secured, that is, modified to allow the CIA and BND to break codes. The operation was codenamed Thesaurus and then renamed Rubicon in 1980s.
Full story here Are you the author? Previous post See more for Next postTags: Business,newsletter